Effects of an α5GABAA inverse agonist on MK-801-induced learning deficits in an incremental repeated acquisition task
- PMID: 25006978
- PMCID: PMC4410981
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000053
Effects of an α5GABAA inverse agonist on MK-801-induced learning deficits in an incremental repeated acquisition task
Abstract
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are essential for several kinds of synaptic plasticity and play a critical role in learning and memory. Deficits in NMDAR functioning may be partially responsible for the learning and memory deficits associated with aging and numerous diseases. Administration of MK-801, a noncompetitive NMDAR antagonist, is commonly used as a preclinical model of NMDAR dysfunction. The objective of this study was to assess the effects of α5GABAA receptor inhibition on learning deficits in the incremental repeated acquisition (IRA) task induced by acute MK-801 administration. The IRA task, commonly used to examine factors that affect learning, begins with a single response and increments to progressively longer chains throughout a single session as behavior meets preset criteria. MK-801 (0.03-0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally), administered 10 min pretesting, produced a significant dose-dependent decrease in measures of IRA performance at doses greater than or equal to 0.25 mg/kg. The MK-801-induced deficit was attenuated after treatment with an α5GABAA receptor inverse agonist, L-655,708 (1 mg/kg, intraperitoneally). The present study provides the focus for, and supports the feasibility of, further in-depth definitive studies examining α5GABAA receptor inhibition as a suitable candidate for the attenuation of NMDAR-related deficits.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
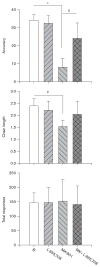
References
-
- Adams MM, Smith TD, Moga D, Gallagher M, Wang Y, Wolfe BB, et al. Hippocampal dependent learning ability correlates with N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor levels in CA3 neurons of young and aged rats. J Comp Neurol. 2001;432:230–243. - PubMed
-
- Atack JR, Alder L, Cook SM, Smith AJ, McKernan RM. In vivo labelling of α5 subunit-containing GABA (A) receptors using the selective radioligand [3 H]L-655,708. Neuropharmacology. 2005;49:220–229. - PubMed
-
- Atack JR, Bayley PJ, Seabrook GR, Wafford KA, McKernan RM, Dawson GR. L-655,708 enhances cognition in rats but is not proconvulsant at a dose selective for alpha5-containing GABA (A) receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2006;51:1023–1029. - PubMed
-
- Bailey JM, Johnson JE, Newland MC. Mechanisms and performance measures in mastery-based incremental repeated acquisition: behavioral and pharmacological analyses. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2010;209:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Bauter MR, Brockel BJ, Pankevich DE, Virgolini MB, Cory-Slechta DA. Glutamate and dopamine in nucleus accumbens core and shell: sequence learning versus performance. Neurotoxicology. 2003;24:227–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

