Flavonoids and Wnt/β-catenin signaling: potential role in colorectal cancer therapies
- PMID: 25007066
- PMCID: PMC4139831
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms150712094
Flavonoids and Wnt/β-catenin signaling: potential role in colorectal cancer therapies
Abstract
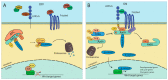
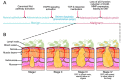
It is now well documented that natural products have played an important role in anticancer therapy. Many studies focus on the ability of these natural compounds to modulate tumor-related signaling pathways and the relationship of these properties to an anticancer effect. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer death among men and women. Therefore, finding strategies to fight against CRC is an emergent health problem. CRC has a strong association with deregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. As some types of natural compounds are capable of modulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling, one important question is whether they could counteract CRC. In this review, we discuss the role of flavonoids, a class of natural compounds, on Wnt/β-catenin regulation and its possible potential for therapeutic usage on colorectal cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The anti-cancer activity of an andrographolide analogue functions through a GSK-3β-independent Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2018 May 21;8(1):7924. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26278-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29784906 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Feb;110:473-481. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.082. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30530050 Review.
-
Raddeanin A inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer through downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2018 Aug 15;207:532-549. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.06.035. Epub 2018 Jul 1. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29972765
-
Targeting lncRNA/Wnt axis by flavonoids: A promising therapeutic approach for colorectal cancer.Phytother Res. 2022 Nov;36(11):4024-4040. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7550. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 36227024 Review.
-
The anthelmintic niclosamide inhibits colorectal cancer cell lines via modulation of the canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling pathway.J Surg Res. 2016 Jun 1;203(1):193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.03.051. Epub 2016 Mar 30. J Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27338550
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Naturally Occurring Small Molecules to Target the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 14;14(2):403. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020403. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic strategies targeting Wnt/β‑catenin signaling for colorectal cancer (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 Jan;49(1):1. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5056. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34713301 Free PMC article.
-
Triphala Extract Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Stem Cells via Suppressing c-Myc/Cyclin D1 and Elevation of Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:649263. doi: 10.1155/2015/649263. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26167492 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive Endogenous RNA (ceRNA) Regulation Network of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA in Colorectal Carcinogenesis.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Jul;64(7):1868-1877. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05506-9. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30734239
-
Computational identification of potential inhibitors targeting cdk1 in colorectal cancer.Front Chem. 2023 Nov 30;11:1264808. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1264808. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 38099190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu R.H. Health benefits of fruit and vegetables are from additive and synergistic combinations of phytochemicals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003;78:517S–520S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

