Safety and tolerability of conserved region vaccines vectored by plasmid DNA, simian adenovirus and modified vaccinia virus ankara administered to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-uninfected adults in a randomized, single-blind phase I trial
- PMID: 25007091
- PMCID: PMC4090156
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101591
Safety and tolerability of conserved region vaccines vectored by plasmid DNA, simian adenovirus and modified vaccinia virus ankara administered to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-uninfected adults in a randomized, single-blind phase I trial
Abstract
Trial design: HIV-1 vaccine development has advanced slowly due to viral antigenic diversity, poor immunogenicity and recently, safety concerns associated with human adenovirus serotype-5 vectors. To tackle HIV-1 variation, we designed a unique T-cell immunogen HIVconsv from functionally conserved regions of the HIV-1 proteome, which were presented to the immune system using a heterologous prime-boost combination of plasmid DNA, a non-replicating simian (chimpanzee) adenovirus ChAdV-63 and a non-replicating poxvirus, modified vaccinia virus Ankara. A block-randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled phase I trial HIV-CORE 002 administered for the first time candidate HIV-1- vaccines or placebo to 32 healthy HIV-1/2-uninfected adults in Oxford, UK and elicited high frequencies of HIV-1-specific T cells capable of inhibiting HIV-1 replication in vitro. Here, detail safety and tolerability of these vaccines are reported.
Methods: Local and systemic reactogenicity data were collected using structured interviews and study-specific diary cards. Data on all other adverse events were collected using open questions. Serum neutralizing antibody titres to ChAdV-63 were determined before and after vaccination.
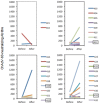
Results: Two volunteers withdrew for vaccine-unrelated reasons. No vaccine-related serious adverse events or reactions occurred during 190 person-months of follow-up. Local and systemic events after vaccination occurred in 27/32 individuals and most were mild (severity grade 1) and predominantly transient (<48 hours). Myalgia and flu-like symptoms were more strongly associated with MVA than ChAdV63 or DNA vectors and more common in vaccine recipients than in placebo. There were no intercurrent HIV-1 infections during follow-up. 2/24 volunteers had low ChAdV-63-neutralizing titres at baseline and 7 increased their titres to over 200 with a median (range) of 633 (231-1533) post-vaccination, which is of no safety concern.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate safety and good tolerability of the pSG2.HIVconsv DNA, ChAdV63.HIVconsv and MVA.HIVconsv vaccines and together with their high immunogenicity support their further development towards efficacy studies.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01151319.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Altfeld M, Addo MM, Rosenberg ES, Hecht FM, Lee PK, et al. (2003) Influence of HLA-B57 on clinical presentation and viral control during acute HIV-1 infection. AIDS 17: 2581–2591. - PubMed
-
- Leslie AJ, Pfafferott KJ, Chetty P, Draenert R, Addo MM, et al. (2004) HIV evolution: CTL escape mutation and reversion after transmission. Nat Med 10: 282–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

