AFLPs and mitochondrial haplotypes reveal local adaptation to extreme thermal environments in a freshwater gastropod
- PMID: 25007329
- PMCID: PMC4090234
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101821
AFLPs and mitochondrial haplotypes reveal local adaptation to extreme thermal environments in a freshwater gastropod
Abstract
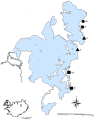
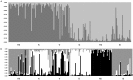
The way environmental variation shapes neutral and adaptive genetic variation in natural populations is a key issue in evolutionary biology. Genome scans allow the identification of the genetic basis of local adaptation without previous knowledge of genetic variation or traits under selection. Candidate loci for divergent adaptation are expected to show higher FST than neutral loci influenced solely by random genetic drift, migration and mutation. The comparison of spatial patterns of neutral markers and loci under selection may help disentangle the effects of gene flow, genetic drift and selection among populations living in contrasting environments. Using the gastropod Radix balthica as a system, we analyzed 376 AFLP markers and 25 mtDNA COI haplotypes for candidate loci and associations with local adaptation among contrasting thermal environments in Lake Mývatn, a volcanic lake in northern Iceland. We found that 2% of the analysed AFLP markers were under directional selection and 12% of the mitochondrial haplotypes correlated with differing thermal habitats. The genetic networks were concordant for AFLP markers and mitochondrial haplotypes, depicting distinct topologies at neutral and candidate loci. Neutral topologies were characterized by intense gene flow revealed by dense nets with edges connecting contrasting thermal habitats, whereas the connections at candidate loci were mostly restricted to populations within each thermal habitat and the number of edges decreased with temperature. Our results suggest microgeographic adaptation within Lake Mývatn and highlight the utility of genome scans in detecting adaptive divergence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kingsolver JG, Ragland GJ, Diamond SE (2009) Evolution in a constant environment: Thermal fluctuations and thermal sensitivity of laboratory and field populations of Manduca sexta . Evolution 63: 537–541. - PubMed
-
- Angilletta MJ (2009) Thermal Adaptation. A Theoretical and Empirical Synthesis. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
-
- Morelissen B, Harley CDG (2007) The effects of temperature on producers, consumers, and plant-herbivore interactions in an intertidal community. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 348: 162–173.
-
- Dillon ME, Wang G, Huey RB (2010) Global metabolic impacts of recent climate warming. Nature 467: 704–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Dryad/10.5061/dryad.3ND75
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

