Haloperidol versus low-potency first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia
- PMID: 25007358
- PMCID: PMC10898321
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009268.pub2
Haloperidol versus low-potency first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Antipsychotic drugs are the core treatment for schizophrenia. Treatment guidelines state that there is no difference in efficacy between antipsychotic compounds, however, low-potency antipsychotic drugs are often clinically perceived as less efficacious than high-potency compounds, and they also seem to differ in their side-effects.
Objectives: To review the effects in clinical response of haloperidol and low-potency antipsychotics for people with schizophrenia.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group Trials Register (July 2010).
Selection criteria: We included all randomised trials comparing haloperidol with first-generation low-potency antipsychotic drugs for people with schizophrenia or schizophrenia-like psychosis.
Data collection and analysis: We extracted data independently. For dichotomous data, we calculated risk ratios (RR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) on an intention-to-treat basis based on a random-effects model. For continuous data, we calculated mean differences (MD), again based on a random-effects model.
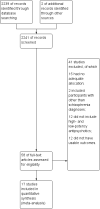
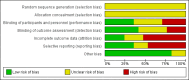
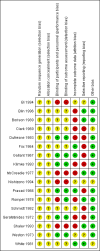
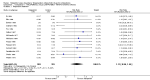
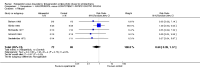
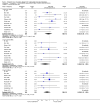
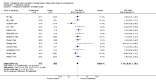
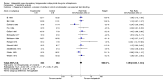
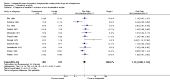
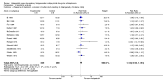
Main results: The review currently includes 17 randomised trials and 877 participants. The size of the included studies was between 16 and 109 participants. All studies were short-term with a study length between two and 12 weeks. Overall, sequence generation, allocation procedures and blinding were poorly reported. We found no clear evidence that haloperidol was superior to low-potency antipsychotic drugs in terms of clinical response (haloperidol 40%, low-potency drug 36%, 14 RCTs, n = 574, RR 1.11, CI 0.86 to 1.44 lowquality evidence). There was also no clear evidence of benefit for either group in acceptability of treatment with equivocal difference in the number of participants leaving the studies early due to any reason (haloperidol 13%, low-potency antipsychotics 17%, 11 RCTs, n = 408, RR 0.82, CI 0.38 to 1.77, low quality evidence). Similar equivocal results were found between groups for experiencing at least one adverse effect (haloperidol 70%, low-potency antipsychotics 35%, 5 RCTs n = 158, RR 1.97, CI 0.69 to 5.66, very low quality evidence ). More participants from the low-potency drug group experienced sedation (haloperidol 14%, low-potency antipsychotics 41%, 2 RCTs, n = 44, RR 0.30, CI 0.11 to 0.82, moderate quality evidence), orthostasis problems (haloperidol 25%, low-potency antipsychotics 71%, 1 RCT, n = 41, RR 0.35, CI 0.16 to 0.78) and weight gain (haloperidol 5%, low-potency antipsychotics 29%, 3 RCTs, n = 88, RR 0.22, CI 0.06 to 0.81). In contrast, the outcome 'at least one movement disorder' was more frequent in the haloperidol group (haloperidol 72%, low-potency antipsychotics 41%, 5 RCTs, n = 170, RR 1.64, CI 1.22 to 2.21, low quality evidence). No data were available for death or quality of life. The results of the primary outcome were robust in several subgroup and sensitivity analyses.
Authors' conclusions: The results do not clearly show a superiority in efficacy of haloperidol compared with low-potency antipsychotics. Differences in adverse events were found for movement disorders, which were more frequent in the haloperidol group, and orthostatic problems, sedation and weight gain, which were more frequent in the low-potency antipsychotic group. The quality of studies was low, and the quality of evidence for the main outcomes of interest varied from moderate to very low, so more newer studies would be needed in order to draw a definite conclusion about whether or not haloperidol is superior or inferior to low-potency antipsychotics.
Conflict of interest statement
Magdolna Tardy ‐ none to declare. Maximilian Huhn ‐ none to declare. Werner Kissling ‐ has received speaker and/or advisory board/consultancy honoraria from Janssen, Sanofi‐Aventis, Johnson and Johnson, Pfizer, Bayer, BMS, Astra Zeneca, Lundbeck, Novartis and EliLilly. Rolf Engel ‐ none to declare. Stefan Leucht ‐ has received honoraria for lectures from Abbvie, Astra Zeneca, BristolMyersSquibb, ICON, EliLilly, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Roche, SanofiAventis, Lundbeck and Pfizer; honoraria for consulting/advisory boards from Roche, EliLilly, Medavante, BristolMyersSquibb, Alkermes, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson and Lundbeck. EliLilly has provided medication for a study with SL as primary investigator.
Figures









Comment in
-
Haloperidol vs. Low-Potency Antipsychotic Drugs for Schizophrenia.Am J Nurs. 2015 Jul;115(7):21. doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000467267.67704.e1. Am J Nurs. 2015. PMID: 26110946 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Bi 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bi Y. A relation study of the extrapyramidal symptoms, serum prolactin levels and clinical response during treatment of antipsychotics. Chinese Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 1994;20(2):70‐3.
Blin 1996 {published data only}
-
- Blin O, Azorin JM, Bouhours P. Antipsychotic and anxiolytic properties of risperidone, haloperidol, and methotrimeprazine in schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1996; Vol. 16, issue 1:38‐44. - PubMed
-
- Blin O, Azorin JM, Bouhours P. Anxiolytic profiles of levomepromazine, haloperidol and risperidone in 62 schizophrenic patients. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. France, 1992; Vol. 51, issue 2:189.
-
- Blin O, Azorin JM, Bouhours P. Anxiolytic profiles of levomepromazine, haloperidol, and risperidone in 62 schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 1992:31‐2.
-
- Blin O, Azorin JM, Bouhours P. Comparison of anxiolytic properties of levomepromazine, haloperidol and risperidone in schizophrenic patients. Biological Psychiatry. France, 1991; Vol. 29:388.
-
- Blin O, Azorin JM, Bouhours P, Fondarai J. Anxiolytic profiles of risperidone, haloperidol, and levomepromazine in schizophrenia: a factorial and regression analysis. Proceedings of the 9th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1993 Jun 6‐12; Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. France, 1993:24.
Borison 1989 {published data only}
-
- Borison RL, Sinha D, Haverstock S, McLarnon MC, Diamond BI. Efficacy and safety of tiospirone vs. haloperidol and thioridazine in a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1989; Vol. 25, issue 2:190‐3. - PubMed
Clark 1969 {published data only}
-
- Clark ML. Haloperidol versus chlorpromazine versus placebo. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1969; Vol. 5, issue 3:57‐9.
Dufresne 1993 {published data only}
-
- Dufresne RL, Valentino D, Kass DJ. Thioridazine improves affective symptoms in schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1993; Vol. 29, issue 2:249‐55. - PubMed
Fox 1964 {published data only}
-
- Fox W, Gobble IF, Clos M. A clinical comparison of trifluperidol, haloperidol and chlorpromazine. Current Therapeutic Research 1964;6(6):409‐15. - PubMed
Gallant 1967 {published data only}
-
- Gallant DM, Bishop M, Guerrero‐Figueroa R. Effects of two butyrophenone compounds on acute schizophrenic patients: speculation on the neurophysiologic sites of action. International Journal of Neuropsychiatry 1967;3(1):53‐60. - PubMed
Klimke 1993 {published data only}
-
- Klimke A, Klieser E, Lehmann E, Miele L. Initial improvement as a criterion for drug choice in acute schizophrenia. Pharmacopsychiatry 1993;26:25‐9. - PubMed
McCreadie 1977 {published data only}
-
- McCreadie RG, MacDonald IM. High dosage haloperidol in chronic schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1977; Vol. 131:310‐6. - PubMed
Nishizono 1994 {published data only}
-
- Nishizono M. A comparative trial of zotepine, chlorpromazine and haloperidol in schizophrenic patients. Neuropsychopharmacology 1994;10:30.
Prasad 1966 {published data only}
-
- Prasad L, Townley MC. Haloperidol and thioridazine in treatment of chronic schizophrenics. Diseases of the Nervous System 1966;27(11):722‐6. - PubMed
Rompel 1978 {published data only}
-
- Rompel H, Segal H. A comparison of the relative efficacy of serenace and chlorpromazine in the treatment of chronic schizophrenics. Journal of International Medical Research 1978; Vol. 6, issue 2:126‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schmidt 1982 {published data only}
-
- Schmidt LG, Schüssler G, Kappes CV, Müller‐Oerlinghausen B. Comparison of higher‐dose haloperidol therapy with perazine standard therapy in acute schizophrenic patients [Vergleich einer höher dosierten Haloperidol‐Therapie mt einer Perazin‐Standard‐Therapie bei akut‐schizophrenen Patienten]. Nervenarzt 1982;53(9):530‐6. - PubMed
Serafetinides 1972 {published data only}
-
- Serafetinides EA, Clark ML. Psychological effects of single dose antipsychotic medication. Biological Psychiatry 1973; Vol. 7, issue 3:263‐7. - PubMed
-
- Serafetinides EA, Collins S, Clark ML. Haloperidol, clopenthixol, and chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. Chemically unrelated antipsychotics as therapeutic alternatives. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1972; Vol. 154, issue 1:31‐42. - PubMed
Shalev 1993 {published data only}
-
- Shalev A, Hermesh H, Rothberg J, Munitz H. Poor neuroleptic response in acutely exacerbated schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1993; Vol. 87, issue 2:86‐91. - PubMed
Weston 1973 {published data only}
-
- Weston MJ, Bentley R, Unwin A, Morris M, Harper MA. A comparative trial of haloperidol and thioridazine: management of chronic schizophrenia. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1973; Vol. 7, issue 1:52‐7. - PubMed
White 1981 {published data only}
-
- White K, Busk J, Eaton E, Gomez G, Razani J, Sloane RB. Dysphoric response to neuroleptics as a predictor of treatment outcome with schizophrenics. A comparative study of haloperidol versus mesoridazine. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1981; Vol. 16, issue 1:34‐8. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Azima 1960 {published data only}
-
- Azima H, Durost, Arthurs D. The effect of R‐1625 (haloperidol) in mental syndromes: a multiblind study. American Journal of Psychiatry 1960; Vol. 117:546‐7. - PubMed
Bagne 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bagne CA, Lewis RF. Evaluating the effects of drugs on behavior and quality of life: an alternative strategy for clinical trials. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1992; Vol. 60:225‐39. - PubMed
Blum 1969 {published data only}
-
- Blum RA, Livingston PB, Shader RI. Changes in cognition, attention and language in acute schizophrenia. Diseases of the Nervous System 1969; Vol. 30, issue 1:31‐6. - PubMed
Cassano 1975 {published data only}
-
- Cassano GB, Castrogiovanni P, Conti L. The computer diagnosis in a multicenter study of psychoactive agents. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1976; Vol. 12, issue 2:22‐4. - PubMed
-
- Cassano GB, Castrogiovanni P, Conti L, Bonollo L. Sulpiride versus haloperidol in schizophrenia: a double‐blind comparative trial. Current Therapeutic Research 1975; Vol. 17, issue 2:189‐201. - PubMed
-
- Castrogiovanni P, Cassano GB, Conti L, Maggini C, Bonollo L, Sarteschi P. An automated diagnostic process (PDA) in clinical psychopharmacology. An exemplification of its use in a sulpiride versus haloperidol comparative trial. International Pharmacopsychiatry 1976; Vol. 11, issue 2:74‐83. - PubMed
Cosar 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cosar B, Candansayar S, Taner E, Isik E. Comparison of efficacy of clozapine, sulpiride, chlorpromazine and haloperidol in chronic schizophrenic patients therapy. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1999; Vol. 9:S287.
Crow 1986 {published data only}
-
- Crow TJ, MacMillan JF, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. A randomised controlled trial of prophylactic neuroleptic treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986; Vol. 148, issue 2:120‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Johnstone EC, Crow J, Johnson AL, MacMillan JF. The northwick park study of first episodes of schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148:115‐20. - PubMed
Davies 2007 {published data only}
-
- Davies LM, Lewis S, Jones PB, Barnes TR, Gaughran F, Hayhurst K, et al. CUtLASS team. Cost‐effectiveness of first‐ versus second‐generation antipsychotic drugs: results from a randomised controlled trial in schizophrenia responding poorly to previous therapy. British Journal of Psychiatry. United Kingdom, 2007; Vol. 191, issue July:14‐22. - PubMed
-
- Jones PB, Batnes TR, Davies L, Dunn G, Lloyd H, Hayhurst KP, et al. Randomized controlled trial of the effect on quality of life of second‐ vs first‐generation antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: Cost Utility of the Latest Antipsychotic Drugs in Schizophrenia Study (CUtLASS 1). Archives of General Psychiatry. United States, 2006; Vol. 63, issue 10:1079‐87. - PubMed
de Lima 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lima MS, Jesus MJ, Breier A, Costa AM, Sena EP, Hotopf M. Quality of life in schizophrenia: a multicenter, randomized, naturalistic, controlled trial comparing olanzapine to first‐generation antipsychotics. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. United States, 2005; Vol. 66, issue 7:831‐8. - PubMed
Dubin 1985 {published data only}
-
- Dubin WR, Waxman HM, Weiss KJ, Ramchandani D, Tavani‐Petrone C. Rapid tranquilization: the efficacy of oral concentrate. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1985; Vol. 46, issue 11:475‐8. - PubMed
Eitan 1992 {published data only}
-
- Eitan N, Levin Y, Ben Artzi E, Levy A, Neumann M. Effects of antipsychotic drugs on memory functions of schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1992; Vol. 85, issue 1:74‐6. - PubMed
Fux 1991 {published data only}
-
- Fux M, Belmaker RH. A controlled comparative study of chlorprothixene vs. haloperidol in chronic schizophrenia. Israel Journal of Psychiatry and Related Sciences 1991; Vol. 28, issue 1:37‐40. - PubMed
Garry 1962 {published data only}
-
- Garry JW, Leonard TJ. Haloperidol: a controlled trial in chronic schizophrenia. Journal of Mental Science 1962; Vol. 108:105‐7. - PubMed
Gerlach 1978 {published data only}
-
- Gerlach J, Simmelsgaard H. Tardive dyskinesia during and following treatment with haloperidol, haloperidol + biperiden, thioridazine, and clozapine. Psychopharmacology 1978; Vol. 59, issue 2:105‐12. - PubMed
Gillis 1977 {published data only}
-
- Gillis JS. The effects of selected antipsychotic drugs of human judgment. Current Therapeutic Research, Clinical and Experimental 1977; Vol. 21, issue 2:224‐32. - PubMed
Giordana 1984 {published data only}
-
- Giordana JY, Frenay S. Comparative study of pipotiazine (in its non‐esterified form) and of haloperidol in acute or subacute psychotic states [Etude comparative de la pipothiazine (dans sa forme non esterifiee) et de l'haloperidol au cours d'etats psychotiques aigus et subaigus]. Psychologie Medicale 1984;16(10):1803‐15.
Gonier 1970 {published data only}
-
- Gonier T, Schiele BC, Vestre ND. A comparison of haloperidol and thioridazine HC1 in chronic treatment‐resistant schizophrenics. Behavioral Neuropsychiatry 1970;2(3):47‐50. - PubMed
Guazzelli 1995 {published data only}
-
- Guazzelli M, Barracchia E, Bertolino A, Bertolino lA, Casacchia M, Ciapparelli A, et al. Clinical effects of l‐sulpiride vs haloperidol in acutely relapsed chronic schizophrenics: therapeutic efficacy on "disorganization"?. Proceedings of the 8th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1995 Sep 30 ‐ Oct 4; Venice, Italy 1995.
Harris 1992 {published data only}
-
- Harris MJ, Panton D, Caligiuri MP, Krull AJ, Tran Johnson TK, Jeste DV. High incidence of tardive dyskinesia in older outpatients on low doses of neuroleptics. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1992; Vol. 28, issue 1:87‐92. - PubMed
Hayano 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hayano T, Kadomae S, Kikuoka M, Imade T, Ikoma Y, Nakatani Y, et al. Pharmacometrics of double‐blind test of two drugs, haloperidol and sultopride (barnetil(R); MS‐5024), on the schizophrenic patients. Journal of the Wakayama Medical Society 1989; Vol. 40, issue 4:607‐20.
Hogan 1992 {published data only}
-
- Hogan TP, Awad AG. Subjective response to neuroleptics and outcome in schizophrenia: a re‐examination comparing two measures. Psychological Medicine 1992; Vol. 22, issue 2:347‐52. - PubMed
Horodnicki 1985 {published data only}
-
- Horodnicki JM, Czekalski S, Jarema M, Kubasiewicz A, Pobocha J, Wdowiak J. Comparison of the effects of chlorprothixene and haloperidol on hypothalamic function in patients with paranoid schizophrenia [Porownanie wplywu chloroprotyksenu i haloperidolu na czynnosc podwzgorza u chorych na schizofrenie paranoidalna]. Psychiatria Polska 1985; Vol. 19, issue 3:181‐7. - PubMed
Lempérière 1962 {published data only}
-
- Lempérière T, Delay J, Pichot P, Piret J. A comparison of the effects of four major antipsychotic drugs (chlorpromazine, thioproperazine, prochlorpremazine and haloperidol) for paraniod schizophrenia [Comparaison de l'action de quatre neuroleptiques majeurs (chlorpromazine, thiopropérazine, prochlorprémazine ethalopéridol) dans les formes paranoides de la schizophrénie]. Neuro‐Psychopharmacology 1962;3:89‐93.
Liu 1996 {published data only}
-
- Liu K, LLung FW. Difference in prolaction response of schizophrenic patients to equivalent doses of haloperidol, remoxipride and sulpiride. Kao Hsiung I Hsueh Ko Hsueh Tsa Chih Kaohsiung (Journal of Medical Sciences) 1996; Vol. 12, issue 12:685‐90. - PubMed
Marjerrison 1971 {published data only}
-
- Marjerrison G, Bowman R, Keogh RP. A comparison of chlorprothixene and haloperidol in acute schizophrenia. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1971; Vol. 16, issue 6:533‐6. - PubMed
Mechri 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mechri A, Fendri C, Ben Othman L, Mekhinini A, Kerkeni A, Gaha L. Effect of first generation antipsychotic treatment on oxidative stress markers in schizophrenia. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2006; Vol. 16, issue Suppl 4:S438.
Minami 1990 {published data only}
-
- Minami H, Miyahara A, Murasaki O, Nakanishi T, Ogawa H, Ohkubo T, et al. Prediction of response to chlorpromazine and haloperidol after test dose. Proceedings of the 17th Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum Congress; 1990 Sep 10‐14; Kyoto, Japan 1990:215.
Mori 1989 {published data only}
-
- Mori A, Kazamatsuri H, Kaneno S, Kamijima K, Kariya T, Murasaki M, et al. A double‐blind comparison of a new benzamide compound YM 09151 with haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia. Rinsho Hyoka (Clinical Evaluation) 1989; Vol. 17, issue 3‐4:349‐77.
Mori 1990 {published data only}
-
- Mori A, Kazamatsuri H, Kaneno S, Kamijima K, Kariya T, Murasaki M, et al. A double‐blind comparison of emonapride with haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia. Proceedings of the 17th Collegium Internationale Neuro‐Psychopharmacologicum Congress; 1990 Sep 10‐14; Kyoto, Japan 1990:296.
Munk‐Andersen 1984 {published data only}
-
- Gerlach J, Behnke K, Heltberg J, Munk‐Anderson E, Nielsen H. Sulpiride and haloperidol in schizophrenia: a double‐blind cross‐over study of therapeutic effect, side effects and plasma concentrations. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985; Vol. 147:283‐8. - PubMed
-
- Munk‐Andersen E, Behnke K, Heltberg J, Nielsen H. Sulpiride versus haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia. A short preliminary report [Sulpirid versus haloperidol i behandling af skizofreni. En kort, praeliminaer rapport]. Nordisk Psykiatrisk Tidsskrift 1984; Vol. 38, issue 4:223‐8.
-
- Munk‐Andersen EM, Behnke K, Heltberg J, Nielsen H, Gerlach J. Sulpiride versus haloperidol, a clinical trial in schizophrenia. A preliminary report. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1984; Vol. 311:31‐41. - PubMed
Nahunek 1982 {published data only}
-
- Nahunek K, Svestka J, Ceskova E, Rysanek R. Blind comparison of oxyprothepin and haloperidol in six‐week treatment periods in schizophrenia. Activitas Nervosa Superior 1982; Vol. 24, issue 4:219‐20.
Okuda 1979 {published data only}
-
- Okuda O, Akaue Y, Okishio Y. The efficacy of sulpiride in the treatment of schizophrenia by the double‐blind method. Yakuri To Chiryo 1979; Vol. 7, issue 2:439‐58.
Palma 1997 {published data only}
-
- Palma Wenzel MI, Parada R, Osorio C, Dorr A, Bauer S. Flupentixol decanoate versus other neuroleptics in chronic schizophrenia [Decanoato de flupentixol versus otros neurolepticos en esquizofrenicos cronicos]. Revista Chilena de Neuropsiquiatria 1997; Vol. 35, issue 1:29‐35.
Rama 1981 {published data only}
-
- Rama Rao V, Bailey J, Bishop M, Coppen A. A clinical and pharmacodynamic evaluation of sulpiride. Psychopharmacology 1981; Vol. 73, issue 1:77‐80. - PubMed
Ropert 1989 {published data only}
-
- Ropert R, Payan C, Allard S. Sultopride versus haloperidol for the treatment of acute psychosis. Results of a multicenter double‐blind controlled trial [Sultopride versus haloperidol dans le traitement des etats psychotiques aigus]. Annales de Psychiatrie 1989; Vol. 4, issue 1:92‐8.
Shvartsburd 1984 {published data only}
-
- Shvartsburd A, Sajadi C, Morton V, Mirabi M, Gordon J, Smith RC. Blood levels of haloperidol and thioridazine during maintenance neuroleptic treatment of schizophrenic outpatients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1984; Vol. 4, issue 4:194‐8. - PubMed
Singh 1975 {published data only}
-
- Singh MM. Dysphoric response to neuroleptic treatment in schizophrenia and its prognostic significance. Diseases of the Nervous System 1976; Vol. 37:191‐6. - PubMed
-
- Singh MM, Kay SR. A comparative study of haloperidol and chlorpromazine in terms of clinical effects and therapeutic reversal with benztropine in schizophrenia. Theoretical implications for potency differences among neuroleptics. Psychopharmacology 1975; Vol. 43, issue 2:103‐13. - PubMed
-
- Singh MM, Kay SR. A longitudinal therapeutic comparison between two prototypic neuroleptics (haloperidol and chlorpromazine) in matched groups of schizophrenics. Nontherapeutic interactions with trihexyphenidyl. Theoretical implications for potency differences. Psychopharmacology 1975; Vol. 43, issue 2:115‐21. - PubMed
-
- Singh MM, Kay SR. Therapeutic reversal with benztropine in schizophrenics: practical and theoretical significance. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1975; Vol. 160, issue 4:258‐66. - PubMed
Smith 1985 {published data only}
-
- Smith RC, Baumgartner R, Burd A, Ravichandran GK, Mauldin M. Haloperidol and thioridazine drug levels and clinical response in schizophrenia: comparison of gas‐liquid chromatography and adioreceptor drug level assays. Psychopharmacology Bulletin. United States, 1985; Vol. 21, issue 1:52‐8. - PubMed
Teja 1975 {published data only}
-
- Teja JS, Grey WH, Clum JM, Warren C. Tranquilizers or anti‐depressanrs for chronic schizophrenics: a long term study. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 1975;9:241‐7. - PubMed
Terminska 1989 {published data only}
-
- Terminska K, Mrowiec W. Comparison of influence of perazine, fluphenazine, trifluoroperazine, chloropromazine and haloperidol on primary and deficit schizophrenic symptoms in patients first hospitalized because of paranoid schizophrenia [Badanie porownawcze wplywu perazyny, flufenazyny, trifluoroperazyny, chloropromazny i haloperydolu na objawy pierwotne i deficytowe pierwszego zachorowania na schizofrenie paranoidalna]. Psychiatria Polska 1989; Vol. 23, issue 1:24‐30. - PubMed
Wang 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wang YC, Cuo JH, Chen JS. The relation of qeeg with the therapeutic effect of antipsychotic drugs. Modern Rehabilitation 2000; Vol. 4, issue 11:12‐3.
Zuoning 1999 {published data only}
-
- Zuoning J, Huang Shu Zheng, Qin Ying Fu, Yamamoto M. Comparative clinical study of nemonapride, a benzamide compound with dopamine D‐2‐like receptor blocking activity, and haloperidol in schizophrenic patients. Research Communications in Biological Psychology and Psychiatry 1999; Vol. 24, issue 1‐2:35‐46.
Additional references
Adams 2013
Altman 1996
Andreasen 2010
APA 1980
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Third Edition (DSM III). Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1980.
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 3rd edition‐ Revised (DSM‐III‐R). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1987.
Asberg 1970
Berger 2003
-
- Berger M. Psychische Erkrankungen. Klinik und Therapie. 2nd Edition. München: Urban & Fischer, 2003.
Bland 1997
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, et al. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices. 3. Comparison of the indices and their use. Therapie 1999;54(4):405‐11. - PubMed
Carpenter 1994
-
- Carpenter WT, Buchanan RW. Schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330:681‐90. - PubMed
Chouinard 1980
-
- Chouinard G, Ross‐Chouinard A, Annable L, Jones BD. Extrapyramidal Symptom Rating Scale. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1980;7:233‐9.
Davis 1974
-
- Davis JM. Overview: maintenance therapy in psychiatry: I. Schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1975;132(12):1237‐45. - PubMed
Davis 1989
-
- Davis JM, Barter JT, Kane JM. Antipsychotic drugs. Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry. Williams and Wilkins, 1989.
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta‐analyses of binary data. Proceedings of the 8th International Cochrane Colloquium; 2000 Oct 25‐28th; Cape Town, South Africa. Cape Town, 2000.
Der‐Simonian 1986
-
- Der‐Simonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:177‐88. - PubMed
DiMascio 1976
-
- DiMascio A, Bernardo DC. A controlled trial of amantadine in drug‐induced extrapyramidal disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry 1976;33:599‐602. - PubMed
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazer LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7:623‐9. - PubMed
Dold 2012
Donnelly 2013
Duggan 2005
Duval 2000
-
- Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel‐plot‐based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics 2000;56(2):455‐63. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JP, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31:140‐9. - PubMed
Falkai 2005
-
- Falkai P, Wobrock T, Lieberman J. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) ‐ Guidelines for biological treatment of schizophrenia, part 1: Acute treatment of schizophrenia. World Journal of Biological Psychiatry 2005;6:132‐91. - PubMed
Feighner 1972
-
- Feighner JP, Robins E, Guze SB, Woodruff RA, Winokur G, Munoz R. Diagnostic criteria for use in psychiatric research. Archives of General Psychiatry 1972;26:57‐63. - PubMed
Fenton 2007
Furukawa 2006
-
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(1):7‐10. - PubMed
Furukawa 2011
-
- Furukawa TA, Akechi T, Wagenpfeil S, Leucht S. Relative indices of treatment effect may be constant across different definitions of response in schizophrenia trials. Schizophrenia Research 2011;126:212‐9. - PubMed
Gaebel 2006
-
- Gaebel W, Falkai P, Weinmann S. Behandlungsleitlinie Schizophrenie. Darmstadt: Steinkopff, 2006.
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC, Ukoumunne OC, Chinn S. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. Clinical Global Impressions Scale. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology (DOTES: Dosage Record and Treatment Emergent Symptom Scale). National Institute of Mental Health, 1976.
Haase 1983
-
- Haase HJ. Dosierung der Neuroleptika. Ein Leitfaden für Klinik und Praxis unter besonderer Berücksichtigung psychotisch Kranker. Erlangen: Perimed fachbuch‐verlagsgesellschaft, 1983.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org..
Jones 2006
-
- Jones PB, Barnes TRE, Davies L. Randomized controlled trial of the effect on quality of life of second‐ vs first‐generation antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia ‐ cost utility of the latest antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia study (CUtLASS 1). Archives of General Psychiatry 2006;63:1079‐86. - PubMed
Kane 1996
-
- Kane JM. Schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;334:34‐41. - PubMed
Kane 2011
-
- Kane JM, Mackle M, Snow‐Adami L, Zhao J, Szegedi A, Panagides J. A randomized placebo‐controlled trial of asenapine for the prevention of relapse of schizophrenia after long‐term treatment. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2011;72(3):349‐55. - PubMed
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Manual. North Tonawanda (NY): Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Kaye 2003
Klein 1969
-
- Klein DF, Davis JM. Diagnosis and Drug Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1969.
Lehman 2004
-
- Lehman AF, Lieberman JA, Dixon LB. Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia, second edition. American Journal of Psychiatry 2004;161:1‐56. - PubMed
Leon 2006
-
- Leon AC, Mallinckrodt CH, Chuang‐Stein C, Archibald DG, Archer GE, Chartier K. Attrition in randomized controlled clinical trials: methodological issues in psychopharmacology. Biological Psychiatry 2006;59:1001‐5. - PubMed
Leucht 2005a
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. What does the PANSS mean?. Schizophrenia Research 2005;79:231‐8. - PubMed
Leucht 2005b
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of brief psychiatric rating scale scores. British Journal of Psychiatry 2005;187:366‐71. - PubMed
Leucht 2009a
-
- Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, Engel R, Li C, Davis JM. A meta‐analysis comparing second‐generation and first‐generation antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Lancet 2009;373:31‐41. - PubMed
Leucht 2009b
-
- Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, Engel RR, Li C, Davis JM. Second‐generation versus first‐generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: a meta‐analysis. Lancet 2009;373(9657):31‐41. - PubMed
Lieberman 2005
-
- Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353:1209‐23. - PubMed
Lohse 2005
-
- Lohse MJ, Lorenzen A, Müller‐Oerlinghausen B. Psychotropic drugs [Psychopharmaka]. Arzneimittel Verordnungs Report 2005:820‐64.
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Bradley C, Adams C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales: a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249‐52. - PubMed
Marvaha 2004
-
- Marwaha S, Johnson S. Schizophrenia and employment ? a review. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 2004;39:337‐49. - PubMed
Moher 2010
NIMH 1985
-
- National Institute of Mental Health. Special feature: rating scales and assessment instruments for use in pediatric psychopharmacology research. Psychopharmacological Bulletin 1985;21(4):714‐1124. - PubMed
Omori 2009
-
- Omori Ichiro M, Wang J, Soares B, Fenton M. Sulpiride versus other antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008126] - DOI
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐12.
Paton 2003
-
- Paton C, Lelliott P, Harrington M. Patterns of antipsychotic and anticholinergic prescribing for hospital inpatients. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2003;17:223‐9. - PubMed
Schneider 1959
-
- Schneider K. Clinical Psychopathology. New York: Grune and Stratton, 1959.
Schünemann 2008
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008:359‐83.
Seeman 1975
-
- Seeman P, Lee T. Antipsychotic drugs: direct correlation between clinical potency and presynaptic action on dopamine neurons. Science 1975;188:1217‐9. - PubMed
Simpson 1970
-
- Simpson EN, Angus JWF. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side‐effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1970;212:11‐9. - PubMed
Soares 1999
Spitzer 1978
-
- Spitzer RL, Robins E. Research diagnostic criteria: rationale and reliability. Archives of General Psychiatry 1978;35(6):773‐82. - PubMed
Tardy 2011b
Tardy 2011c
Tardy 2011d
Tardy 2011e
Trikalinos 2004
-
- Trikalinos TA, Churchill R, Ferri M, Leucht S, Tuunainen A, Wahlbeck K, Ioannidis JP, EU‐PSI project. Effect sizes in cumulative meta‐analyses of mental health randomized trials evolved over time. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2004;57(11):1124‐30. - PubMed
Tsuang 1978
-
- Tsuang MT. Suicide in schizophrenics, manics, depressives, and surgical controls: a comparison with general population suicide mortality. Archives of General Psychiatry 1978;35:153‐5. - PubMed
Whitehead 2002
WHO 1978
-
- World Health Organization. The Ninth Revision of the International Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD‐9). Geneva: World Health Organization, 1978.
WHO 1992
-
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision (ICD‐10). Geneva: World Health Organization, 1992.
Xia 2009
-
- Xia J, Adams CE, Bhagat N, Bhagat V, Bhoopathi P, El‐Sayeh H, et al. Loss to outcomes stakeholder survey: the LOSS study. Psychiatric Bulletin 2009;33(7):254‐7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

