Genome and transcriptome sequencing identifies breeding targets in the orphan crop tef (Eragrostis tef)
- PMID: 25007843
- PMCID: PMC4119204
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-581
Genome and transcriptome sequencing identifies breeding targets in the orphan crop tef (Eragrostis tef)
Abstract
Background: Tef (Eragrostis tef), an indigenous cereal critical to food security in the Horn of Africa, is rich in minerals and protein, resistant to many biotic and abiotic stresses and safe for diabetics as well as sufferers of immune reactions to wheat gluten. We present the genome of tef, the first species in the grass subfamily Chloridoideae and the first allotetraploid assembled de novo. We sequenced the tef genome for marker-assisted breeding, to shed light on the molecular mechanisms conferring tef's desirable nutritional and agronomic properties, and to make its genome publicly available as a community resource.
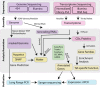
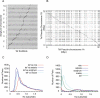
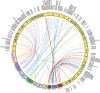
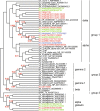
Results: The draft genome contains 672 Mbp representing 87% of the genome size estimated from flow cytometry. We also sequenced two transcriptomes, one from a normalized RNA library and another from unnormalized RNASeq data. The normalized RNA library revealed around 38000 transcripts that were then annotated by the SwissProt group. The CoGe comparative genomics platform was used to compare the tef genome to other genomes, notably sorghum. Scaffolds comprising approximately half of the genome size were ordered by syntenic alignment to sorghum producing tef pseudo-chromosomes, which were sorted into A and B genomes as well as compared to the genetic map of tef. The draft genome was used to identify novel SSR markers, investigate target genes for abiotic stress resistance studies, and understand the evolution of the prolamin family of proteins that are responsible for the immune response to gluten.
Conclusions: It is highly plausible that breeding targets previously identified in other cereal crops will also be valuable breeding targets in tef. The draft genome and transcriptome will be of great use for identifying these targets for genetic improvement of this orphan crop that is vital for feeding 50 million people in the Horn of Africa.
Figures


References
-
- Agricultural Sample Survey for 2012/13. Ethiopia: Statistical Bulletin Addis Ababa; 2013.
-
- Umeta M, West CE, Fufa H. Content of zinc, iron, calcium and their absorption inhibitors in foods commonly consumed in Ethiopia. J Food Compos Anal. 2005;18(8):803–817. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2004.09.008. - DOI
-
- Alaunyte I, Stojceska V, Plunkett A, Ainsworth P, Derbyshire E. Improving the quality of nutrient-rich Teff (Eragrostis tef) breads by combination of enzymes in straight dough and sourdough breadmaking. J Cereal Sci. 2012;55(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2011.09.005. - DOI
-
- Tye-Din JA, Stewart JA, Dromey JA, Beissbarth T, van Heel DA, Tatham A, Henderson K, Mannering SI, Gianfrani C, Jewell DP, Hill AV, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J, Anderson RP. Comprehensive, quantitative mapping of T cell epitopes in gluten in celiac disease. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2(41):41ra51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

