Antagonism of the prostaglandin E2 EP1 receptor in MDCK cells increases growth through activation of Akt and the epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 25007872
- PMCID: PMC4154115
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00510.2013
Antagonism of the prostaglandin E2 EP1 receptor in MDCK cells increases growth through activation of Akt and the epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
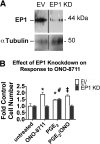
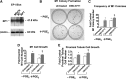
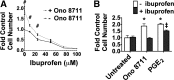
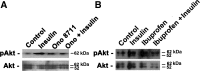
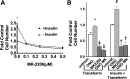
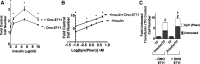
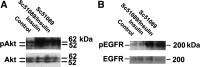
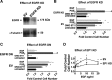
The actions of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in the kidney are mediated by G protein-coupled E-prostanoid (EP) receptors, which affect renal growth and function. This report examines the role of EP receptors in mediating the effects of PGE2 on Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell growth. The results indicate that activation of Gs-coupled EP2 and EP4 by PGE2 results in increased growth, while EP1 activation is growth inhibitory. Indeed, two EP1 antagonists (ONO-8711 and SC51089) stimulate, rather than inhibit, MDCK cell growth, an effect that is lost following an EP1 knockdown. Similar observations were made with M1 collecting duct and rabbit kidney proximal tubule cells. ONO-8711 even stimulates growth in the absence of exogenous PGE2, an effect that is prevented by ibuprofen (indicating a dependence upon endogenous PGE2). The involvement of Akt was indicated by the observation that 1) ONO-8711 and SC51089 increase Akt phosphorylation, and 2) MK2206, an Akt inhibitor, prevents the increased growth caused by ONO-8711. The involvement of the EGF receptor (EGFR) was indicated by 1) the increased phosphorylation of the EGFR caused by SC51089 and 2) the loss of the growth-stimulatory effect of ONO-8711 and SC51089 caused by the EGFR kinase inhibitor AG1478. The growth-stimulatory effect of ONO-8711 was lost following an EGFR knockdown, and transduction of MDCK cells with a dominant negative EGFR. These results support the hypothesis that 1) signaling via the EP1 receptor involves Akt as well as the EGFR, and 2), EP1 receptor pharmacology may be employed to prevent the aberrant growth associated with a number of renal diseases.
Keywords: EP receptors; kidney epithelial cell growth; prostaglandin E2.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
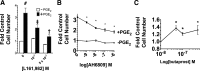
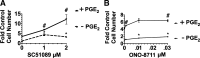
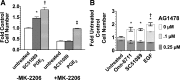
Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E2 increases proximal tubule fluid reabsorption, and modulates cultured proximal tubule cell responses via EP1 and EP4 receptors.Lab Invest. 2015 Sep;95(9):1044-55. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.79. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Lab Invest. 2015. PMID: 26121313
-
Cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin E2 promotes human cholangiocarcinoma cell growth and invasion through EP1 receptor-mediated activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and Akt.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 24;280(25):24053-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500562200. Epub 2005 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2005. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 17;290(29):17806. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A115.500562. PMID: 15855163 Retracted.
-
Neuroprotection by PGE2 receptor EP1 inhibition involves the PTEN/AKT pathway.Neurobiol Dis. 2008 Mar;29(3):543-51. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2007.11.010. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Neurobiol Dis. 2008. PMID: 18178094 Free PMC article.
-
[Cooperation of two subtypes of PGE2 receptor, Gi coupled EP3 and Gs coupled EP2 or EP4 subtype].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003 Oct;123(10):837-43. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.123.837. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14577329 Review. Japanese.
-
EP1 receptor: Devil in emperors coat.J Cell Biochem. 2023 Aug;124(8):1105-1114. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30436. Epub 2023 Jul 14. J Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37450673 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal proximal tubule Na,K-ATPase is controlled by CREB-regulated transcriptional coactivators as well as salt-inducible kinase 1.Cell Signal. 2015 Dec;27(12):2568-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.09.015. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 26432356 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of mPGES-1 exacerbates renal fibrosis and inflammation in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;312(1):F121-F133. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00231.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27784694 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism for the anticancer activity of aspirin and salicylates.Int J Oncol. 2019 Apr;54(4):1256-1270. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4701. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30720135 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 Enhances Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication in Clonal Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 28;22(11):5813. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115813. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071686 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 in the Regulation of Water Transport in Renal Collecting Ducts.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 27;18(12):2539. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122539. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29186911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alessi DR. Discovery of PDK1, one of the missing links in insulin signal transduction. Colworth Medal Lecture. Biochem Soc Trans 29: 1–14, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Aoudjit L, Potapov A, Takano T. Prostaglandin E2 promotes cell survival of glomerular epithelial cells via the EP4 receptor. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290: F1534–F1542, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bonvalet JP, Pradelles P, Farman N. Segmental synthesis and actions of prostaglandins along the nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 253: F377–F387, 1987 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

