Microglia and inflammation: conspiracy, controversy or control?
- PMID: 25008043
- PMCID: PMC11113719
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1670-8
Microglia and inflammation: conspiracy, controversy or control?
Abstract
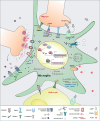
Microglial cells contribute to normal function of the central nervous system (CNS). Besides playing a role in the innate immunity, they are also involved in neuronal plasticity and homeostasis of the CNS. While microglial cells get activated and undergo phenotypic changes in different disease contexts, they are far from being the "villains" in the CNS. Mounting evidence indicates that microglial dysfunction can exacerbate the pathogenesis of several diseases in the CNS. Several molecular mechanisms tightly regulate the production of inflammatory and toxic factors released by microglia. These mechanisms involve the interaction with other glial cells and neurons and the fine regulation of signaling and transcription activation pathways. The purpose of this review is to discuss microglia activation and to highlight the molecular pathways that can counteract the detrimental role of microglia in several neurologic diseases. Recent work presented in this review support that the understanding of microglial responses can pave the way to design new therapies for inflammatory diseases of the CNS.
Figures
References
-
- Schulz C, et al. A lineage of myeloid cells independent of Myb and hematopoietic stem cells. Science. 2012;336(6077):86–90. - PubMed
-
- Aloisi F, Ria F, Adorini L. Regulation of T-cell responses by CNS antigen-presenting cells: different roles for microglia and astrocytes. Immunol Today. 2000;21(3):141–147. - PubMed
-
- Eichhoff G, Brawek B, Garaschuk O. Microglial calcium signal acts as a rapid sensor of single neuron damage in vivo . Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(5):1014–1024. - PubMed
-
- Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F. Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo . Science. 2005;308(5726):1314–1318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

