Early failure of frontline rituximab-containing chemo-immunotherapy in diffuse large B cell lymphoma does not predict futility of autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation
- PMID: 25008330
- PMCID: PMC4194275
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.06.036
Early failure of frontline rituximab-containing chemo-immunotherapy in diffuse large B cell lymphoma does not predict futility of autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation
Abstract
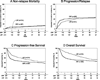
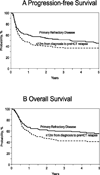
The poor prognosis for patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who relapse within 1 year of initial diagnosis after first-line rituximab-based chemo-immunotherapy has created controversy about the role of autologous transplantation (HCT) in this setting. We compared autologous HCT outcomes for chemosensitive DLBCL patients between 2000 and 2011 in 2 cohorts based on time to relapse from diagnosis. The early rituximab failure (ERF) cohort consisted of patients with primary refractory disease or those with first relapse within 1 year of initial diagnosis. The ERF cohort was compared with those relapsing >1 year after initial diagnosis (late rituximab failure [LRF] cohort). ERF and LRF cohorts included 300 and 216 patients, respectively. Nonrelapse mortality (NRM), progression/relapse, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) of ERF versus LRF cohorts at 3 years were 9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 6% to 13%) versus 9% (95% CI, 5% to 13%), 47% (95% CI, 41% to 52%) versus 39% (95% CI, 33% to 46%), 44% (95% CI, 38% to 50%) versus 52% (95% CI, 45% to 59%), and 50% (95% CI, 44% to 56%) versus 67% (95% CI, 60% to 74%), respectively. On multivariate analysis, ERF was not associated with higher NRM (relative risk [RR], 1.31; P = .34). The ERF cohort had a higher risk of treatment failure (progression/relapse or death) (RR, 2.08; P < .001) and overall mortality (RR, 3.75; P <.001) within the first 9 months after autologous HCT. Beyond this period, PFS and OS were not significantly different between the ERF and LRF cohorts. Autologous HCT provides durable disease control to a sizeable subset of DLBCL despite ERF (3-year PFS, 44%) and remains the standard-of-care in chemosensitive DLBCL regardless of the timing of disease relapse.
Keywords: Aggressive lymphoma; Autologous transplantation; Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; Early failure; High-dose therapy; Non-Hodgkin lymphoma; Rituximab.
Copyright © 2014 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Philip T, Armitage JO, Spitzer G, et al. High-dose therapy and autologous bone marrow transplantation after failure of conventional chemotherapy in adults with intermediate-grade or high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N.Engl.J.Med. 1987;316:1493–1498. - PubMed
-
- Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N.Engl.J.Med. 1995;333:1540–1545. - PubMed
-
- Verdonck LF, van Putten WL, Hagenbeek A, et al. Comparison of CHOP chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow transplantation for slowly responding patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N.Engl.J.Med. 1995;332:1045–1051. - PubMed
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N.Engl.J.Med. 2002;346:235–242. - PubMed
-
- Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d'Etudes des Lymphomes de l'Adulte. Blood. 2010;116:2040–2045. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

