An unusual case of iatrogenic haemoptysis
- PMID: 25008338
- PMCID: PMC4091135
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-204673
An unusual case of iatrogenic haemoptysis
Abstract
Summary Transbronchial needle aspiration (TBNA) of the hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes and lung masses is a powerful tool in the diagnostic evaluation of mediastinal adenopathies including malignancies. As its use becomes more widespread, few cases have been reported with complications. We present a case of a 57-year-old man who was transferred to our institution for uncontrolled haemoptysis following endobronchial ultrasound-guided TBNA. At our institution, emergent bronchoscopy revealed a large clot distal to the right upper lobe bronchus without a visible fistula tract. A CT pulmonary angiogram and a subsequent pulmonary angiogram showed an aneurysm originating from the right superior pulmonary vein. Management was conservative with strict blood pressure control and lowering the left atrial pressure allowed spontaneous resolution of the bleed.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
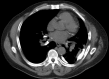
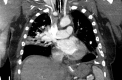
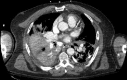
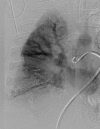
References
-
- Fielding DI, Kurimoto N. EBUS-TBNA/staging of lung cancer. Clin Chest Med 2013;34:385–94 - PubMed
-
- Groth SS, Andrade RS. Endobronchial and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: a must for thoracic surgeons. Ann Thorac Surg 2010;89:S2079–83 - PubMed
-
- Vincent B, Huggins JT, Doelken P, et al. Successful real-time endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration of a hilar lung mass obtained by traversing the pulmonary artery. J Thorac Oncol 2006;1:362–4 - PubMed
-
- Varela-Lema L, Fernández-Villar A, Ruano-Ravina A. Effectiveness and safety of endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial needle aspiration: a systematic review. Eur Respir J 2009;33:1156–64 - PubMed
-
- Garwood S, Judson MA, Silvestri G, et al. Endobronchial ultrasound for the diagnosis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Chest 2007;132:1298–304 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
