Pertussis-specific memory B-cell and humoral IgG responses in adolescents after a fifth consecutive dose of acellular pertussis vaccine
- PMID: 25008903
- PMCID: PMC4178576
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00280-14
Pertussis-specific memory B-cell and humoral IgG responses in adolescents after a fifth consecutive dose of acellular pertussis vaccine
Abstract
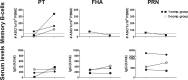
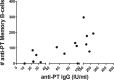
In order to impede the increase in pertussis incidence in the adolescent group, a school-leaving booster dose administered at the age of 14 to 16 years will be introduced in Sweden in 2016. Preceding this introduction, an open-label, randomized, multicenter, clinical trial without a control group and with blinded analysis was performed, investigating both safety and immunogenicity. Reported here are the memory B-cell and serological responses detected in a smaller cohort (n = 34) of the 230 subjects recruited to the study. All subjects had received primary vaccination consisting of three doses of diphtheria-tetanus-5-component pertussis (DTaP5) vaccine, at 3, 5, and 12 months of age, and a tetanus-low-dose diphtheria-5-component pertussis (Tdap5) vaccine booster at 5.5 years. In this study, the subjects were randomly assigned and received either a Tdap1 or Tdap5 booster. Of the 230 participants, 34 subjects had samples available for evaluation of IgG-producing memory B-cell responses. Both vaccine groups had significant increases in pertussis toxin-specific serum IgG levels, but only the 1-component group showed significant increases in pertussis toxin-specific memory B cells. The 5-component group had significant increases in filamentous hemagglutinin- and pertactin-specific memory B-cell and serum IgG levels; these were not seen in the 1-component group, as expected. In conclusion, this study shows that a 5th consecutive dose of an acellular pertussis vaccine induces B-cell responses in vaccinated adolescents. (This study has been registered at EudraCT under registration no. 2008-008195-13 and at ClinicalTrials.gov under registration no. NCT00870350.).
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Nilsson L, von Segebaden K, Bergström J, Nuru N. 2013. Pertussis surveillance in Sweden: fifteen year report. Swedish Institute for Communicable Disease Control, Solna, Sweden
-
- Sato Y, Kimura M, Fukumi H. 1984. Development of a pertussis component vaccine in Japan. Lancet 1(8369):122–126 - PubMed
-
- Olin P, Rasmussen F, Gustafsson L, Hallander HO, Heijbel H. 1997. Randomised controlled trial of two-component, three-component, and five-component acellular pertussis vaccines compared with whole-cell pertussis vaccine. Lancet 350:1569–1577 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

