HIV-1 gp120 activates the STAT3/interleukin-6 axis in primary human monocyte-derived dendritic cells
- PMID: 25008924
- PMCID: PMC4178808
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00307-14
HIV-1 gp120 activates the STAT3/interleukin-6 axis in primary human monocyte-derived dendritic cells
Abstract
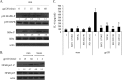
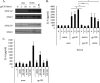
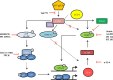
Dendritic cells (DCs) are fundamental for the initiation of immune responses and are important players in AIDS immunopathogenesis. The modulation of DC functional activities represents a strategic mechanism for HIV-1 to evade immune surveillance. Impairment of DC function may result from bystander effects of HIV-1 envelope proteins independently of direct HIV-1 infection. In this study, we report that exposure of immature monocyte-derived DCs (MDDCs) to HIV-1 R5 gp120 resulted in the CCR5-dependent production of interleukin-6 (IL-6) via mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/NF-κB pathways. IL-6 in turn activated STAT3 by an autocrine loop. Concomitantly, gp120 promoted an early activation of STAT3 that further contributed to IL-6 induction. This activation paralleled a concomitant upregulation of the STAT3 inhibitor PIAS3. Notably, STAT3/IL-6 pathway activation was not affected by the CCR5-specific ligand CCL4. These results identify STAT3 as a key signaling intermediate activated by gp120 in MDDCs and highlight the existence of a virus-induced dysregulation of the IL-6/STAT3 axis. HIV-1 gp120 signaling through STAT3 may provide an explanation for the impairment of DC function observed upon HIV exposure.
Importance: This study provides new evidence for the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways triggered by HIV-1 gp120 in human DCs in the absence of productive infection, emphasizing a role of aberrant signaling in early virus-host interaction, contributing to viral pathogenesis. We identified STAT3 as a key component in the gp120-mediated signaling cascade involving MAPK and NF-κB components and ultimately leading to IL-6 secretion. STAT3 now is recognized as a key regulator of DC functions. Thus, the identification of this transcription factor as a signaling molecule mediating some of gp120's biological effects unveils a new mechanism by which HIV-1 may deregulate DC functions and contribute to AIDS pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
HIV-1 gp120 influences the expression of microRNAs in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells via STAT3 activation.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jun 27;16(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1673-3. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26116514 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 gp120 protein downregulates Nef induced IL-6 release in immature dentritic cells through interplay of DC-SIGN.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59073. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059073. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554973 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C activation is required for CCR5-dependent, NF-kB-driven CCL2 secretion elicited in response to HIV-1 gp120 in human primary macrophages.Blood. 2008 Apr 1;111(7):3355-63. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-08-104901. Epub 2008 Jan 18. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18203956 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage activation through CCR5- and CXCR4-mediated gp120-elicited signaling pathways.J Leukoc Biol. 2003 Nov;74(5):676-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0503206. Epub 2003 Jul 22. J Leukoc Biol. 2003. PMID: 12960231 Review.
-
Role of gp120 in dendritic cell dysfunction in HIV infection.J Leukoc Biol. 2006 Nov;80(5):994-1000. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0306135. Epub 2006 Aug 15. J Leukoc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16912071 Review.
Cited by
-
gp120 Envelope Glycoproteins of HIV-1 Group M Subtype A and Subtype B Differentially Affect Gene Expression in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3536. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043536. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834948 Free PMC article.
-
Increased IL-6 expression precedes reliable viral detection in the rhesus macaque brain during acute SIV infection.JCI Insight. 2021 Oct 22;6(20):e152013. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.152013. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34676832 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic modulation of the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway for HIV shock and kill.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Mar 5;14:1354502. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1354502. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38505285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Coinfection of Infant Tonsil Epithelium May Synergistically Promote both HIV-1 and HCMV Spread and Infection.J Virol. 2021 Aug 25;95(18):e0092121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00921-21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34232730 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 gp120 influences the expression of microRNAs in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells via STAT3 activation.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jun 27;16(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1673-3. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26116514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller CJ, Hu J. 1999. T cell-tropic simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) and simian-human immunodeficiency viruses are readily transmitted by vaginal inoculation of rhesus macaques, and Langerhans' cells of the female genital tract are infected with SIV. J. Infect. Dis. 179(Suppl 3):S413–S417. 10.1086/314795 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

