Androgen receptor and its splice variant, AR-V7, differentially regulate FOXA1 sensitive genes in LNCaP prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 25008967
- PMCID: PMC4160387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.06.013
Androgen receptor and its splice variant, AR-V7, differentially regulate FOXA1 sensitive genes in LNCaP prostate cancer cells
Abstract
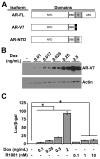
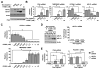
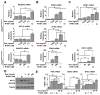
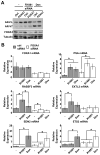
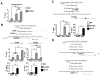
Prostate cancer (PCa) is an androgen-dependent disease, and tumors that are resistant to androgen ablation therapy often remain androgen receptor (AR) dependent. Among the contributors to castration-resistant PCa are AR splice variants that lack the ligand-binding domain (LBD). Instead, they have small amounts of unique sequence derived from cryptic exons or from out of frame translation. The AR-V7 (or AR3) variant is constitutively active and is expressed under conditions consistent with CRPC. AR-V7 is reported to regulate a transcriptional program that is similar but not identical to that of AR. However, it is unknown whether these differences are due to the unique sequence in AR-V7, or simply to loss of the LBD. To examine transcriptional regulation by AR-V7, we have used lentiviruses encoding AR-V7 (amino acids 1-627 of AR with the 16 amino acids unique to the variant) to prepare a derivative of the androgen-dependent LNCaP cells with inducible expression of AR-V7. An additional cell line was generated with regulated expression of AR-NTD (amino acids 1-660 of AR); this mutant lacks the LBD but does not have the AR-V7 specific sequence. We find that AR and AR-V7 have distinct activities on target genes that are co-regulated by FOXA1. Transcripts regulated by AR-V7 were similarly regulated by AR-NTD, indicating that loss of the LBD is sufficient for the observed differences. Differential regulation of target genes correlates with preferential recruitment of AR or AR-V7 to specific cis-regulatory DNA sequences providing an explanation for some of the observed differences in target gene regulation.
Keywords: Androgen receptor; Cell biology; Nuclear receptors; Prostate cancer; Transcription.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

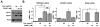
References
-
- Agoulnik IU, Krause WC, Bingman WE, Rahman HT, Amrikachi M, Ayala GE, et al. Repressors of androgen and progesterone receptor action. J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 15;278(33):31136–48. - PubMed
-
- Agoulnik IU, Vaid A, Bingman WE, Erdeme H, Frolov A, Smith CL, et al. Role of SRC-1 in the promotion of prostate cancer cell growth and tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2005 Sep 1;65(17):7959–67. - PubMed
-
- Agoulnik IU, Vaid A, Nakka M, Alvarado M, Bingman WE, Erdem H, et al. Androgens modulate expression of transcription intermediary factor 2, an androgen receptor coactivator whose expression level correlates with early biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006 Nov 1;66(21):10594–602. - PubMed
-
- Bai W, Weigel NL. Phosphorylation of Ser211 in the chicken progesterone receptor modulates its transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 31;271(22):12801–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

