Synucleins regulate the kinetics of synaptic vesicle endocytosis
- PMID: 25009269
- PMCID: PMC4087213
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4787-13.2014
Synucleins regulate the kinetics of synaptic vesicle endocytosis
Abstract
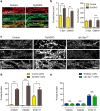
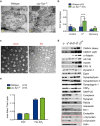
Genetic and pathological studies link α-synuclein to the etiology of Parkinson's disease (PD), but the normal function of this presynaptic protein remains unknown. α-Synuclein, an acidic lipid binding protein, shares high sequence identity with β- and γ-synuclein. Previous studies have implicated synucleins in synaptic vesicle (SV) trafficking, although the precise site of synuclein action continues to be unclear. Here we show, using optical imaging, electron microscopy, and slice electrophysiology, that synucleins are required for the fast kinetics of SV endocytosis. Slowed endocytosis observed in synuclein null cultures can be rescued by individually expressing mouse α-, β-, or γ-synuclein, indicating they are functionally redundant. Through comparisons to dynamin knock-out synapses and biochemical experiments, we suggest that synucleins act at early steps of SV endocytosis. Our results categorize α-synuclein with other familial PD genes known to regulate SV endocytosis, implicating this pathway in PD.
Keywords: AP180; Parkinson's disease; endocytosis; membrane bending; presynaptic; synaptobrevin.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/349364-13$15.00/0.
Figures






References
-
- Anwar S, Peters O, Millership S, Ninkina N, Doig N, Connor-Robson N, Threlfell S, Kooner G, Deacon RM, Bannerman DM, Bolam JP, Chandra SS, Cragg SJ, Wade-Martins R, Buchman VL. Functional alterations to the nigrostriatal system in mice lacking all three members of the synuclein family. J Neurosci. 2011;31:7264–7274. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6194-10.2011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blondeau F, Ritter B, Allaire PD, Wasiak S, Girard M, Hussain NK, Angers A, Legendre-Guillemin V, Roy L, Boismenu D, Kearney RE, Bell AW, Bergeron JJ, McPherson PS. Tandem MS analysis of brain clathrin-coated vesicles reveals their critical involvement in synaptic vesicle recycling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:3833–3838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308186101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
