Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and thyroid dysfunction: a systematic review
- PMID: 25009382
- PMCID: PMC4081681
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8102
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and thyroid dysfunction: a systematic review
Abstract
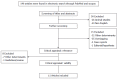
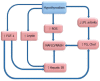
Thyroid hormones are totally involved in the regulation of body weight, lipid metabolism, and insulin resistance. Therefore it is anticipated that thyroid hormones may have a role in the pathogenesis of non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). In this study, we reviewed the current literature on the association between thyroid dysfunction and NAFLD/NASH. A search for English language medical literature reporting an association between thyroid dysfunction and NAFLD/NASH in humans was conducted across PubMed, ISI Web of Science, and Scopus in August, 2013. Out of 140 studies initially identified through the search, 11 relevant articles were included in the final review. Thyroid dysfunctions in the form of overt or subclinical hypothyroidism are prevalent among patients with NAFLD/NASH. Hypothyroidism appears to be an independent risk factor for NAFLD/NASH in some studies; however, other newly published studies failed to find such an association. The results of the studies on the role of thyroid abnormalities in NAFLD/NASH are inconsistent, and further research is recommended to determine the relationship between hypothyroidism and NAFLD/NASH and the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: Hypothyroidism; Non alcoholic fatty liver disease; Non alcoholic steatohepatitis; Pathophysiology; Risk factor; Thyroid dysfunction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Statins for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 27;2013(12):CD008623. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008623.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24374462 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Liver Diseases: NAFLD, NASH, Fibrosis, Cirrhosis-A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 9;14(24):5261. doi: 10.3390/nu14245261. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36558421 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin sensitisers in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Nov;15(38):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta15380. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 22059955 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional supplementation for nonalcohol-related fatty liver disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 19;7(7):CD013157. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013157.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34280304 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological interventions for non-alcohol related fatty liver disease (NAFLD): an attempted network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 30;3(3):CD011640. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011640.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28358980 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Increased apolipoprotein A5 expression in human and rat non-alcoholic fatty livers.Pathology. 2015 Jun;47(4):341-8. doi: 10.1097/PAT.0000000000000251. Pathology. 2015. PMID: 25938357 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Altered Thyroid Hormone Mechanisms in the Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction Associated with Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): A Systematic Review.Metabolites. 2022 Jul 22;12(8):675. doi: 10.3390/metabo12080675. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35893242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid dysfunction and hepatic steatosis in overweight children and adolescents.Pediatr Obes. 2017 Feb;12(1):67-74. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12110. Epub 2016 Feb 14. Pediatr Obes. 2017. PMID: 26877190 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Dysfunction and Dysmetabolic Syndrome: The Need for Enhanced Thyrovigilance Strategies.Int J Endocrinol. 2021 Mar 29;2021:9641846. doi: 10.1155/2021/9641846. eCollection 2021. Int J Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33859689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) and Thyroid Function in Childhood Obesity: A Vicious Circle?Children (Basel). 2024 Feb 15;11(2):244. doi: 10.3390/children11020244. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Law K, Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2010;14:591–604. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P. GI epidemiology: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:883–889. - PubMed
-
- Amarapurkar D, Kamani P, Patel N, Gupte P, Kumar P, Agal S, Baijal R, Lala S, Chaudhary D, Deshpande A. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: population based study. Ann Hepatol. 2007;6:161–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

