Tight junction physiology of pleural mesothelium
- PMID: 25009499
- PMCID: PMC4067758
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00221
Tight junction physiology of pleural mesothelium
Abstract
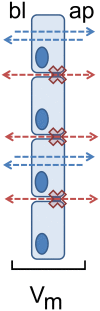
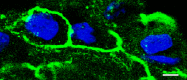
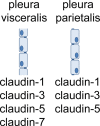
Pleura consists of visceral and parietal cell layers, producing a fluid, which is necessary for lubrication of the pleural space. Function of both mesothelial cell layers is necessary for the regulation of a constant pleural fluid volume and composition to facilitate lung movement during breathing. Recent studies have demonstrated that pleural mesothelial cells show a distinct expression pattern of tight junction proteins which are known to ubiquitously determine paracellular permeability. Most tight junction proteins provide a sealing function to epithelia, but some have been shown to have a paracellular channel function or ambiguous properties. Here we provide an in-depth review of the current knowledge concerning specific functional contribution of these proteins determining transport and barrier function of pleural mesothelium.
Keywords: claudins; mesothelial cells; pleura; tight junctions; tissue barrier.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tight junction proteins contribute to barrier properties in human pleura.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Mar 15;175(3):331-5. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2010.12.012. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21187167
-
Physiology and pathophysiology of pleural fluid turnover.Eur Respir J. 2002 Dec;20(6):1545-58. doi: 10.1183/09031936.02.00062102. Eur Respir J. 2002. PMID: 12503717 Review.
-
Channel functions of claudins in the organization of biological systems.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Sep 1;1862(9):183344. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183344. Epub 2020 May 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32442419 Review.
-
Claudins of intestine and nephron - a correlation of molecular tight junction structure and barrier function.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011 Jan;201(1):133-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02148.x. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011. PMID: 20518752 Review.
-
Pleural Effusion.2024 Aug 31. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Aug 31. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 28846252 Free Books & Documents.
Cited by
-
Toll-like Receptor 2 Mediates VEGF Overexpression and Mesothelial Hyperpermeability in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2846. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032846. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769168 Free PMC article.
-
Lung-Mimetic Hydrofoam Sealant to Treat Pulmonary Air Leak.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 May;13(13):e2303026. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303026. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38279961 Free PMC article.
-
Pleural fluid microbiota as a biomarker for malignancy and prognosis.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 8;13(1):2229. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29001-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36755121 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Ouabain Modulates Expression of Claudins in Rat Intestine and Cerebral Blood Vessels.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 17;21(14):5067. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145067. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32709081 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of the Claudin Interactome in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Evaluation of the Effect of Disease Phenotype, Asbestos Exposure, and CDKN2A Deletion Status.Front Physiol. 2017 Mar 21;8:156. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00156. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28377727 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

