Electroacupuncture treatment improves neurological function associated with regulation of tight junction proteins in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury
- PMID: 25009574
- PMCID: PMC4070389
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/989340
Electroacupuncture treatment improves neurological function associated with regulation of tight junction proteins in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Electroacupuncture Treatment Improves Neurological Function Associated with Regulation of Tight Junction Proteins in Rats with Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury".Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:898474. doi: 10.1155/2015/898474. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26664412 Free PMC article.
Abstract
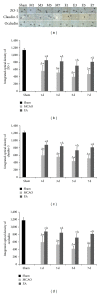
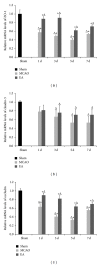
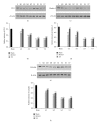
Strategies to develop effective neuroprotective therapy to reduce brain damage and related behavioral deficits in stroke patients are of great significance. Electroacupuncture (EA), which derives from traditional Chinese medicine, may be effective as a complementary and alternative method for promoting recovery of neurological function and quality of life. Adult Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into 3 groups: (1) sham, (2) middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model groups of 2 h MCAO followed by 1, 3, 5, or 7 d of reperfusion, and (3) EA groups of 2 h MCAO followed by 1, 3, 5, or 7 d of reperfusion. EA groups received EA therapy by needling at GV20 and left ST36. The results show that EA therapy improved the neurological function and reduced infarct volume, confirmed by modified neurological severity scores and TTC staining. Real-time PCR, immunohistochemistry, and western blot assay verified that EA upregulated the expression of tight junction (TJ) claudin-5, occludin, and zonula occluding-1 from 1 to 7 d after reperfusion. Our findings suggest that EA reduces brain damage and related behavioral deficits via upregulation of the TJ proteins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of acupuncture at GV20 and ST36 on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2, aquaporin 4, and aquaporin 9 in rats subjected to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.PLoS One. 2014 May 14;9(5):e97488. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097488. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24828425 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on efficacy specificity of electroacupuncture at "Zusanli "(ST36) and "Baihui" (GV20) in cerebral ischemia and inflammatory pain rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020 Oct 25;45(10):823-8. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.190738. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020. PMID: 33788449 Chinese.
-
[Electroacupuncture Combined with Intracerebral Injection of VEGF Improves Neurological Dysfunction Possibly by Down-regulating Expression of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Related Proteins ATF 6, etc. in Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury Rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018 Jun 25;43(6):341-6. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.170908. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018. PMID: 30091538 Chinese.
-
Effect of Electroacupuncture on Neurological Deficit and Activity of Clock and Bmal1 in Cerebral Ischemic Rats.Curr Med Sci. 2020 Dec;40(6):1128-1136. doi: 10.1007/s11596-020-2295-9. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Curr Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33428141
-
Electroacupuncture pretreatment attenuates blood‑brain barrier disruption following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):2027-34. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3672. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25936438
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Aug;44(4):734-744. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240610.004. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39066534 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Involved in the Neuroprotection of Electroacupuncture Therapy for Ischemic Stroke.Front Neurosci. 2018 Dec 11;12:929. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00929. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corrigendum to "Electroacupuncture Treatment Improves Neurological Function Associated with Regulation of Tight Junction Proteins in Rats with Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury".Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:898474. doi: 10.1155/2015/898474. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26664412 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture at GV20 and ST36 Improves the Recovery of Behavioral Activity in Rats Subjected to Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Jun 14;16:909512. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.909512. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35775011 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Acupoints and Combinations with Potential to Treat Vascular Dementia: A Data Mining Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:310591. doi: 10.1155/2015/310591. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26294922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM. Stroke. The Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1612–1623. - PubMed
-
- Chen S-H, Sun H, Xu H, Zhang Y-M, Gao Y, Li S. Effects of acupuncture of “Baihui”(GV 20) and “Zusanli”(ST 36) on expression of cerebral IL-1beta and TNF-alpha proteins in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2012;37(6):470–475. - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Hong L, Huang Y, Chen S, Sun H. The expression of MMP-9 and ICAM-1 in rats with cerebral ischemic /reperfusion treated by acupuncture. Basic & Clinical Medicine. 2010;30(7):731–736.
-
- Xu D, Du W, Zhao L, Davey AK, Wang J. The neuroprotective effects of isosteviol against focal cerebral ischemia injury induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Planta Medica. 2008;74(8):816–821. - PubMed
-
- Nagahiro S, Uno M, Sato K, Goto S, Morioka M, Ushio Y. Pathophysiology and treatment of cerebral ischemia. Journal of Medical Investigation. 1998;45(1-2):57–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

