PAR-2, IL-4R, TGF-β and TNF-α in bronchoalveolar lavage distinguishes extrinsic allergic alveolitis from sarcoidosis
- PMID: 25009615
- PMCID: PMC4079423
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1776
PAR-2, IL-4R, TGF-β and TNF-α in bronchoalveolar lavage distinguishes extrinsic allergic alveolitis from sarcoidosis
Abstract
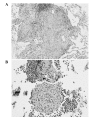
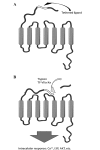
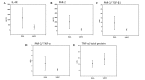
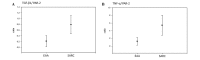
Sarcoidosis (SARC) and extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) share certain markers, making a differential diagnosis difficult even with histopathological investigation. In lung tissue, proteinase-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) is primarily investigated with regard to epithelial and inflammatory perspectives. Varying levels of certain chemokines can be a useful tool for distinguishing EAA and SARC. Thus, in the present study, differences in the levels of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin-4 receptor (IL-4R) and PAR-2 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were compared, using an ELISA method, between 14 patients with EAA and six patients with SARC. Statistically significant higher levels of IL-4R, PAR-2 and the PAR-2/TGF-β1 and PAR-2/TNF-α ratios were observed in EAA patients as compared with SARC patients. Furthermore, the ratios of TNF-α/total protein, TGF-β1/PAR-2 and TNF-α/PAR-2 were significantly lower in EAA patients than in SARC patients. The results indicated a higher detection of PAR-2 in EAA samples in association with TNF-α and TGF-β levels. As EAA and PAR-2 in parallel belong to the Th2-mediated pathway, the results significantly indicated an association between this receptor and etiology. In addition, the results indicated that SARC is predominantly a granulomatous inflammatory disease, thus, higher levels of TNF-α are observed. Therefore, the detection of PAR-2 and investigated chemokines in BALF may serve as a useful tool in the differential diagnosis between EAA and SARC.
Keywords: extrinsic allergic alveolitis; interleukin-4 receptor; proteinase-activated receptor-2; sarcoidosis; transforming growth factor-β; tumor necrosis factor-α.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage cell profiles and proteins concentrations can be used to phenotype extrinsic allergic alveolitis patients.Multidiscip Respir Med. 2019 Mar 12;14:13. doi: 10.1186/s40248-019-0175-6. eCollection 2019. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 30911386 Free PMC article.
-
Role of interleukin 4 and its receptor in clinical presentation of chronic extrinsic allergic alveolitis: a pilot study.Multidiscip Respir Med. 2013 May 30;8(1):35. doi: 10.1186/2049-6958-8-35. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2013. PMID: 23721656 Free PMC article.
-
Is the different T helper cell activity in sarcoidosis and extrinsic allergic alveolitis also reflected by the cellular bronchoalveolar lavage fluid profile?Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1997 Mar;14(1):31-8. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1997. PMID: 9186987
-
Production of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by alveolar macrophages in sarcoidosis and extrinsic allergic alveolitis.Chest. 2005 Jan;127(1):251-6. doi: 10.1378/chest.127.1.251. Chest. 2005. PMID: 15653992
-
Cytokine gene polymorphisms and BALF cytokine levels in interstitial lung diseases.Respir Med. 2009 May;103(5):773-9. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2008.11.006. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Respir Med. 2009. PMID: 19117745
Cited by
-
Metabolic hormones, apolipoproteins, adipokines, and cytokines in the alveolar lining fluid of healthy adults: compartmentalization and physiological correlates.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 7;10(4):e0123344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123344. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25848795 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial Score and Concentrations of IL-4Rα, PAR-2, and MMP-7 in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Could Be Useful Markers for Distinguishing Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Apr 13;11(4):693. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11040693. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924683 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage cell profiles and proteins concentrations can be used to phenotype extrinsic allergic alveolitis patients.Multidiscip Respir Med. 2019 Mar 12;14:13. doi: 10.1186/s40248-019-0175-6. eCollection 2019. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 30911386 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Is There a Role for Biomarkers?Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;13(2):565. doi: 10.3390/life13020565. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Facco M, Cabrelle A, Teramo A, et al. Sarcoidosis is a Th1/Th17 multisystem disorder. Thorax. 2011;66:144–150. - PubMed
-
- Mitaka K, Miyazaki Y, Yasui M, et al. Th2-biased immune responses are important in a murine model of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011;154:264–274. - PubMed
-
- Barrera L, Mendoza F, Zuñiga J, et al. Functional diversity of T-cell subpopulations in subacute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:44–55. - PubMed
-
- van der Poll T, de Boer JD, Levi M. The effect of inflammation on coagulation and vice versa. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2011;24:273–278. - PubMed
-
- Petäjä J. Inflammation and coagulation. An overview Thromb Res. 2011;127(Suppl 2):S34–S37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
