Regulatory mechanism of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate is mediated by nuclear factor-κB and inhibits neutrophil accumulation in ARDS mice
- PMID: 25009629
- PMCID: PMC4079437
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1738
Regulatory mechanism of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate is mediated by nuclear factor-κB and inhibits neutrophil accumulation in ARDS mice
Abstract
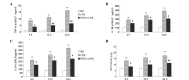
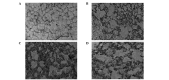
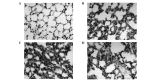
The aim of the present study was to investigate the regulatory mechanism of nuclear factor (NF)-κB on polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) accumulation and the inflammatory response in lung tissues with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), as well as the therapeutic effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC). Mouse models of ARDS were established by intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). BALB/c mice were divided into control, LPS and PDTC + LPS groups. The expression of PMN adhesion molecules, CD11b/CD18 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), were detected by immunohistochemistry, while the protein expression levels of NF-κB p65 in the lung tissue were analyzed by western blot analysis. In addition, flow cytometry was used to investigate the apoptosis rate of PMNs in the bronchoalveolar fluid, and the expression levels of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity were also determined. Following an intraperitoneal injection of LPS, alveolar septum rupture, pulmonary interstitial hyperemia and PMN infiltration in the alveolar was observed. The protein expression of p65 in the pulmonary cytoplasm decreased, while the expression of p65 in the nucleus increased. The levels of IL-8, IL-1β and TNF-α increased and the high expression status was maintained for 24 h. As the time increased, CD11b/CD18 and ICAM-1 expression increased, as well as MPO activity, while the apoptosis of PMNs was delayed. Compared with the LPS group, the expression of p65 in the pulmonary cytoplasm and the PMN apoptosis rate increased following PDTC intervention, while the expression of p65 in the nucleus decreased, as well as the expression levels of the cytokines and MPO activity. Therefore, PDTC reduced the production of inflammatory cytokines via the NF-κB pathway, which reduced the activation of PMNs in the lung tissue and promoted PMN apoptosis.
Keywords: CD11b/CD18; acute respiratory distress syndrome; intercellular adhesion molecule-1; nuclear factor-κB; pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate.
Figures


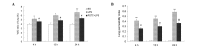


Similar articles
-
Regulatory effect of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant, epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide 78 and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on pulmonary neutrophil aggregation mediated by nuclear factor-κB in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome mice.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Sep;12(3):1785-1794. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3520. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27602092 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997 Nov;17(5):608-16. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.17.5.2661. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9374112
-
[Impact and mechanism of NEMO binding domain peptide on pulmonary inflammation and apoptosis of lung tissues in mice with acute respiratory distress syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Apr;33(4):410-415. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201106-00704. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 34053482 Chinese.
-
[Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B attenuates multiple organ injury following ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: an experiment with rats].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Jan 24;86(4):237-41. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16677502 Chinese.
-
Inhibition of NF-κB by Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Prevents the Inflammatory Response in a Ligature-Induced Peri-Implantitis Model: A Canine Study.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(2):610-625. doi: 10.1159/000492997. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30165363
Cited by
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity: Involvement of mTOR/IKK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Nov;59(11):6903-6917. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03004-0. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36053437
-
Regulatory effect of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant, epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide 78 and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on pulmonary neutrophil aggregation mediated by nuclear factor-κB in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome mice.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Sep;12(3):1785-1794. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3520. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27602092 Free PMC article.
-
PPAR-α improves the recovery of lung function following acute respiratory distress syndrome by suppressing the level of TGF-β1.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Jul;16(1):49-56. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6562. Epub 2017 May 10. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28498479 Free PMC article.
-
An Unsettled Promise: The Newborn Piglet Model of Neonatal Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (NARDS). Physiologic Data and Systematic Review.Front Physiol. 2019 Oct 30;10:1345. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01345. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31736777 Free PMC article.
-
Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza Ameliorate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats by Regulating the Toll-Like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Jan 29;2018:3017571. doi: 10.1155/2018/3017571. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29619068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- Kuo MY, Liao MF, Chen FL, et al. Luteolin attenuates the pulmonary inflammatory response involves abilities of antioxidation and inhibition of MAPK and NF-κB pathways in mice with endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Food Chem Toxicol. 2011;49:2660–2666. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia M, Moochhala S. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Pathol. 2004;202:145–156. - PubMed
-
- Giebelen IA, van Westerloo DJ, LaRosa GJ, et al. Local stimulation of alpha7 cholinergic receptors inhibits LPS-induced TNF-alpha release in the mouse lung. Shock. 2007;28:700–703. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
