β-lapachone-Induced Apoptosis of Human Gastric Carcinoma AGS Cells Is Caspase-Dependent and Regulated by the PI3K/Akt Pathway
- PMID: 25009698
- PMCID: PMC4060078
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2014.026
β-lapachone-Induced Apoptosis of Human Gastric Carcinoma AGS Cells Is Caspase-Dependent and Regulated by the PI3K/Akt Pathway
Abstract
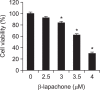
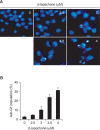
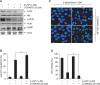
β-lapachone is a naturally occurring quinone that selectively induces apoptotic cell death in a variety of human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo; however, its mechanism of action needs to be further elaborated. In this study, we investigated the effects of β-lapachone on the induction of apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma AGS cells. β-lapachone significantly inhibited cellular proliferation, and some typical apoptotic characteristics such as chromatin condensation and an increase in the population of sub-G1 hypodiploid cells were observed in β-lapachone-treated AGS cells. Treatment with β-lapachone caused mitochondrial transmembrane potential dissipation, stimulated the mitochondria-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway, as indicated by caspase-9 activation, cytochrome c release, Bcl-2 downregulation and Bax upregulation, as well as death receptor-mediated extrinsic apoptotic pathway, as indicated by activation of caspase-8 and truncation of Bid. This process was accompanied by activation of caspase-3 and concomitant with cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. The general caspase inhibitor, z-VAD-fmk, significantly abolished β-lapachone-induced cell death and inhibited growth. Further analysis demonstrated that the induction of apoptosis by β-lapachone was accompanied by inactivation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. The PI3K inhibitor LY29004 significantly increased β-lapachone-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition. Taken together, these findings indicate that the apoptotic activity of β-lapachone is probably regulated by a caspase-dependent cascade through activation of both intrinsic and extrinsic signaling pathways, and that inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling may contribute to β-lapachone-mediated AGS cell growth inhibition and apoptosis induction.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Caspase; PI3K/Akt; β-lapachone.
Figures




References
-
- Ang KL, Shi DL, Keong WW, Epstein RJ. Up-regulated Akt signaling adjacent to gastric cancers: implications for screening and chemoprevention. Cancer Lett. 2005;225:53–59. - PubMed
-
- Binutu OA, Adesogan KE, Okogun JI. Antibacterial and antifungal compounds from Kigelia pinnata. Planta Med. 1996;62:352–353. - PubMed
-
- Boothman DA, Trask DK, Pardee AB. Inhibition of potentially lethal DNA damage repair in human tumor cells by β-lapachone, an activator of topoisomerase I. Cancer Res. 1989;49:605–612. - PubMed
-
- Carnero A, Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Link W, Leal JF. The PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in cancer, therapeutic implications. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2008;8:187–198. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

