Amelioration of Cognitive Dysfunction in APP/PS1 Double Transgenic Mice by Long-Term Treatment of 4-O-Methylhonokiol
- PMID: 25009704
- PMCID: PMC4060074
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2014.030
Amelioration of Cognitive Dysfunction in APP/PS1 Double Transgenic Mice by Long-Term Treatment of 4-O-Methylhonokiol
Abstract
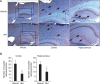
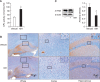
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease without known ways to cure. A key neuropathologic manifestation of the disease is extracellular deposition of beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ). Specific mechanisms underlying the development of the disease have not yet been fully understood. In this study, we investigated effects of 4-O-methylhonokiol on memory dysfunction in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice. 4-O-methylhonokiol (1 mg/kg for 3 month) significantly reduced deficit in learning and memory of the transgenic mice, as determined by the Morris water maze test and step-through passive avoidance test. Our biochemical analysis suggested that 4-O-methylhonokiol ameliorated Aβ accumulation in the cortex and hippocampus via reduction in beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 expression. In addition, 4-O-methylhonokiol attenuated lipid peroxidation and elevated glutathione peroxidase activity in the double transgenic mice brains. Thus, suppressive effects of 4-O-methylhonokiol on Aβ generation and oxidative stress in the brains of transgenic mice may be responsible for the enhancement in cognitive function. These results suggest that the natural compound has potential to intervene memory deficit and progressive neurodegeneration in AD patients.
Keywords: 4-O-methylhonokiol; APP/PS1 double transgenic; Alzheimer’s disease; Antioxidant; Beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme.
Figures


Similar articles
-
4-O-methylhonokiol attenuated memory impairment through modulation of oxidative damage of enzymes involving amyloid-β generation and accumulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;27(1):127-41. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110545. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21799245
-
4-O-methylhonokiol prevents memory impairment in the Tg2576 transgenic mice model of Alzheimer's disease via regulation of β-secretase activity.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;29(3):677-90. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111835. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22330831
-
6-Methyluracil derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015;27 Suppl 1:S69-71. doi: 10.3233/JRS-150694. Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015. PMID: 26639718
-
Atorvastatin ameliorates cognitive impairment, Aβ1-42 production and Tau hyperphosphorylation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Jun;31(3):693-703. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9803-4. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 26883430
-
Huatuo Zaizao pill ameliorates cognitive impairment of APP/PS1 transgenic mice by improving synaptic plasticity and reducing Aβ deposition.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 May 29;18(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2237-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29843688 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
4'-O-methylhonokiol increases levels of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol in mouse brain via selective inhibition of its COX-2-mediated oxygenation.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 May 13;12:89. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0307-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 25962384 Free PMC article.
-
Advancement in modeling of Alzheimer's disease: a comprehensive review of preclinical screening platforms.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Aug 6;17:1646551. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1646551. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40842652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ames dwarf mutation attenuates Alzheimer's disease phenotype of APP/PS1 mice.Neurobiol Aging. 2016 Apr;40:22-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.12.021. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Neurobiol Aging. 2016. PMID: 26973101 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors in Multitarget Paradigm Associated with the Endocannabinoid System.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 20;22(3):1001. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031001. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33498245 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ai J, Sun LH, Che H, Zhang R, Zhang TZ, Wu WC, Su XL, Chen X, Yang G, Li K, Wang N, Ban T, Bao YN, Guo F, Niu HF, Zhu YL, Zhu XY, Zhao SG, Yang BF. MicroRNA-195 protects against dementia induced by chronic brain hypoperfusion via its anti-amyloidogenic effect in rats. J Neurosci. 2013;33:3989–4001. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS. Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1997;19:939–945. - PubMed
-
- Bourne KZ, Ferrari DC, Lange-Dohna C, Rossner S, Wood TG, Perez-Polo JR. Differential regulation of BACE1 promoter activity by nuclear factor-kappaB in neurons and glia upon exposure to beta-amyloid peptides. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85:1194–1204. - PubMed
-
- Chen CH, Zhou W, Liu S, Deng Y, Cai F, Tone M, Tone Y, Tong Y, Song W. Increased NF-kappaB signalling up-regulates BACE1 expressionand its therapeutic potential in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012;15:77–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

