Amelioration of Cognitive Dysfunction in APP/PS1 Double Transgenic Mice by Long-Term Treatment of 4-O-Methylhonokiol
- PMID: 25009704
- PMCID: PMC4060074
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2014.030
Amelioration of Cognitive Dysfunction in APP/PS1 Double Transgenic Mice by Long-Term Treatment of 4-O-Methylhonokiol
Abstract
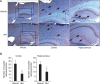
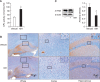
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease without known ways to cure. A key neuropathologic manifestation of the disease is extracellular deposition of beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ). Specific mechanisms underlying the development of the disease have not yet been fully understood. In this study, we investigated effects of 4-O-methylhonokiol on memory dysfunction in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice. 4-O-methylhonokiol (1 mg/kg for 3 month) significantly reduced deficit in learning and memory of the transgenic mice, as determined by the Morris water maze test and step-through passive avoidance test. Our biochemical analysis suggested that 4-O-methylhonokiol ameliorated Aβ accumulation in the cortex and hippocampus via reduction in beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 expression. In addition, 4-O-methylhonokiol attenuated lipid peroxidation and elevated glutathione peroxidase activity in the double transgenic mice brains. Thus, suppressive effects of 4-O-methylhonokiol on Aβ generation and oxidative stress in the brains of transgenic mice may be responsible for the enhancement in cognitive function. These results suggest that the natural compound has potential to intervene memory deficit and progressive neurodegeneration in AD patients.
Keywords: 4-O-methylhonokiol; APP/PS1 double transgenic; Alzheimer’s disease; Antioxidant; Beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme.
Figures


References
-
- Ai J, Sun LH, Che H, Zhang R, Zhang TZ, Wu WC, Su XL, Chen X, Yang G, Li K, Wang N, Ban T, Bao YN, Guo F, Niu HF, Zhu YL, Zhu XY, Zhao SG, Yang BF. MicroRNA-195 protects against dementia induced by chronic brain hypoperfusion via its anti-amyloidogenic effect in rats. J Neurosci. 2013;33:3989–4001. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Ratovitski T, van Lare J, Lee MK, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Price DL, Sisodia SS. Accelerated amyloid deposition in the brains of transgenic mice coexpressing mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid precursor proteins. Neuron. 1997;19:939–945. - PubMed
-
- Bourne KZ, Ferrari DC, Lange-Dohna C, Rossner S, Wood TG, Perez-Polo JR. Differential regulation of BACE1 promoter activity by nuclear factor-kappaB in neurons and glia upon exposure to beta-amyloid peptides. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85:1194–1204. - PubMed
-
- Chen CH, Zhou W, Liu S, Deng Y, Cai F, Tone M, Tone Y, Tong Y, Song W. Increased NF-kappaB signalling up-regulates BACE1 expressionand its therapeutic potential in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012;15:77–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

