Differential diagnoses of overgrowth syndromes: the most important clinical and radiological disease manifestations
- PMID: 25009745
- PMCID: PMC4070411
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/947451
Differential diagnoses of overgrowth syndromes: the most important clinical and radiological disease manifestations
Abstract
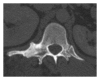
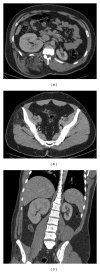
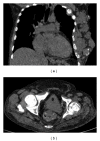
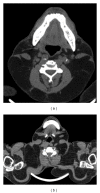
Overgrowth syndromes comprise a heterogeneous group of diseases that are characterized by excessive tissue development. Some of these syndromes may be associated with dysfunction in the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)/PI3K/AKT pathway, which results in an increased expression of the insulin receptor. In the current review, four overgrowth syndromes were characterized (Proteus syndrome, Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome, Madelung's disease, and neurofibromatosis type I) and illustrated using cases from our institution. Because these syndromes have overlapping clinical manifestations and have no established genetic tests for their diagnosis, radiological methods are important contributors to the diagnosis of many of these syndromes. The correlation of genetic discoveries and molecular pathways that may contribute to the phenotypic expression is also of interest, as this may lead to potential therapeutic interventions.
Figures
References
-
- Visser R, Kant SG, Wit JM, Breung MH. Overgrowth syndromes: from classical to new. Pediatric Endocrinology Reviews. 2009;6(3):375–394. - PubMed
-
- Neylon OM, Werther GA, Sabin MA. Overgrowth syndromes. Current Opinion in Pediatrics. 2012;24(4):505–511. - PubMed
-
- Bentov I, Werner H. IGF, IGF receptor and overgrowth syndromes. Pediatric Endocrinology Reviews. 2004;1(4):352–360. - PubMed
-
- Barker KT, Houlston RS. Overgrowth syndromes: is dysfunctional PI3-kinase signalling a unifying mechanism? European Journal of Human Genetics. 2003;11(9):665–670. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

