Redox status in mammalian cells and stem cells during culture in vitro: critical roles of Nrf2 and cystine transporter activity in the maintenance of redox balance
- PMID: 25009780
- PMCID: PMC4085355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.04.008
Redox status in mammalian cells and stem cells during culture in vitro: critical roles of Nrf2 and cystine transporter activity in the maintenance of redox balance
Abstract
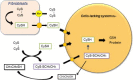
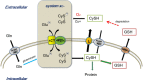
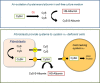
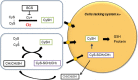
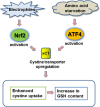
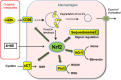
Culturing cells and tissues in vitro has provided valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms regulating redox signaling in cells with implications for medicine. However, standard culture techniques maintain mammalian cells in vitro under an artificial physicochemical environment such as ambient air and 5% CO2. Oxidative stress is caused by the rapid oxidation of cysteine to cystine in culture media catalyzed by transition metals, leading to diminished intracellular cysteine and glutathione (GSH) pools. Some cells, such as fibroblasts and macrophages, express cystine transport activity, designated as system [Formula: see text], which enables cells to maintain these pools to counteract oxidative stress. Additionally, many cells have the ability to activate the redox sensitive transcription factor Nrf2, a master regulator of cellular defenses against oxidative stress, and to upregulate xCT, the subunit of the [Formula: see text] transport system leading to increases in cellular GSH. In contrast, some cells, including lymphoid cells, embryonic stem cells and iPS cells, express relatively low levels of xCT and cannot maintain cellular cysteine and GSH pools. Thus, fibroblasts have been used as feeder cells for the latter cell types based on their ability to supply cysteine. Other key Nrf2 regulated gene products include heme oxygenase 1, peroxiredoxin 1 and sequestosome1. In macrophages, oxidized LDL activates Nrf2 and upregulates the scavenger receptor CD36 forming a positive feedback loop to facilitate removal of the oxidant from the vascular microenvironment. This review describes cell type specific responses to oxygen derived stress, and the key roles that activation of Nrf2 and membrane transport of cystine and cysteine play in the maintenance and proliferation of mammalian cells in culture.
Keywords: 2-Mercaptoethanol; 4HNE, 4-hydroxynonenal; BCS, bathocuproine sulfonate; CD36; Cystine transporter; ES cells, embryonic stem cells; Embryonic stem cells; Feeder cells; Glutathione; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; Lymphocytes; MRPs, multidrug resistance-associated proteins; Nrf2; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Oxygen; Prx1, peroxiredoxin 1; SQSTM1, sequestosome1; iPS cells; iPS cells, induced pluripotent stem cells; oxLDL, oxidized low density lipoprotein; xCT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of xCT and activity of system xc(-) are regulated by NRF2 in human breast cancer cells in response to oxidative stress.Redox Biol. 2015 Aug;5:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 25827424 Free PMC article.
-
Biological insights in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Biol Med. 2023 Jun 28;20(7):500-18. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0108. Cancer Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37381723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Nrf2 in bone marrow-derived macrophages impairs antigen-driven CD8(+) T cell function by limiting GSH and Cys availability.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Jun;83:77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25687825
-
Activation of KEAP1/NRF2 stress signaling involved in the molecular basis of hemin-induced cytotoxicity in human pro-erythroid K562 cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 May;175:113900. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113900. Epub 2020 Mar 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32156661
-
Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:645-657. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.022. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23892355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
d-Cysteine supplementation partially protects against ferroptosis induced by xCT dysfunction via increasing the availability of glutathione.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2022 Jul;71(1):48-54. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.21-143. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35903611 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing Nrf2 Activity as a Treatment Approach in Neuropsychiatry.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 May;58(5):2158-2182. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02212-w. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33411248 Review.
-
The Cutaneous Physiological Redox: Essential to Maintain but Difficult to Define.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 1;9(10):942. doi: 10.3390/antiox9100942. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33019510 Free PMC article.
-
A thiol-bound drug reservoir enhances APR-246-induced mutant p53 tumor cell death.EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Feb 5;13(2):e10852. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201910852. Epub 2020 Dec 14. EMBO Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33314700 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis induction by engineered liposomes for enhanced tumor therapy.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2025 Aug 14;16:1325-1349. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.16.97. eCollection 2025. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40837737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- FS/13/66/30445/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/10/59/28533/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG / 13 / 1 / 29801/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- PG/13/1/29801/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS / 10 / 59 / 28533/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

