Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway Activation in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Its Therapeutic Targeting
- PMID: 25009801
- PMCID: PMC4067595
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00160
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway Activation in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Its Therapeutic Targeting
Abstract
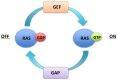
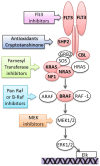
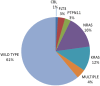
Deregulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway is a common event in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and is caused by point mutation, gene deletion, and chromosomal translocation of a vast array of gene types, highlighting its importance in leukemia biology. Pathway activation can be therapeutically exploited and may guide new therapies needed for relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia and other high risk subgroups.
Keywords: Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway; acute lymphoblastic leukemia; targeted therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CREBBP knockdown enhances RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling in Ras pathway mutated acute lymphoblastic leukemia but does not modulate chemotherapeutic response.Haematologica. 2017 Apr;102(4):736-745. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.145177. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 27979926 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in leukemia therapy.Leukemia. 2011 Jul;25(7):1080-94. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.66. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21494257 Review.
-
Mutation of genes affecting the RAS pathway is common in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer Res. 2008 Aug 15;68(16):6803-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0101. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18701506
-
The Ras/Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway induces autocrine-paracrine growth inhibition via the leukemia inhibitory factor/JAK/STAT pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;23(2):543-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.2.543-554.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12509453 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction mediated by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway from cytokine receptors to transcription factors: potential targeting for therapeutic intervention.Leukemia. 2003 Jul;17(7):1263-93. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402945. Leukemia. 2003. PMID: 12835716 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomics improves risk stratification of adults with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia enrolled in measurable residual disease-oriented trials.Haematologica. 2023 Apr 1;108(4):969-980. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.281196. Haematologica. 2023. PMID: 36325893 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Co-expression and Regulatory Network Analysis Uncover the Relapse Factor and Mechanism of T Cell Acute Leukemia.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Sep 7;12:184-194. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 May 29. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 30195757 Free PMC article.
-
A novel somatic mutation in ACD induces telomere lengthening and apoptosis resistance in leukemia cells.BMC Cancer. 2015 Sep 7;15:621. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1639-5. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26345285 Free PMC article.
-
MEK1 is required for the development of NRAS-driven leukemia.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80113-80130. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12555. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27741509 Free PMC article.
-
DAXX promotes ovarian cancer ascites cell proliferation and migration by activating the ERK signaling pathway.J Ovarian Res. 2018 Oct 18;11(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13048-018-0462-4. J Ovarian Res. 2018. PMID: 30336783 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

