Interaction of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and aerobic granular sludge: biosorption and microbial degradation
- PMID: 25009812
- PMCID: PMC4058842
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/274620
Interaction of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and aerobic granular sludge: biosorption and microbial degradation
Abstract
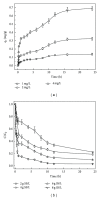
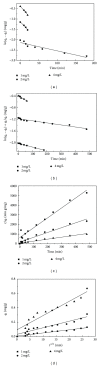
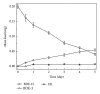
As a new category of persistent organic pollutants, polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) have become ubiquitous global environmental contaminants. No literature is available on the aerobic biotransformation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209). Herein, we investigated the interaction of PBDEs with aerobic granular sludge. The results show that the removal of BDE-209 from wastewater is mainly via biosorption onto aerobic granular sludge. The uptake capacity increased when temperature, contact time, and sludge dosage increased or solution pH dropped. Ionic strength had a negative influence on BDE-209 adsorption. The modified pseudo first-order kinetic model was appropriate to describe the adsorption kinetics. Microbial debromination of BDE-209 did not occur during the first 30 days of operation. Further study found that aerobic microbial degradation of 4,4(')-dibromodiphenyl ether happened with the production of lower BDE congeners.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bioremediation of wastewaters with decabromodiphenyl ether by anaerobic granular sludge.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015 Apr 1;128:522-527. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015. PMID: 25784301
-
Aerobic biodegradation of selected polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in wastewater sewage sludge.Chemosphere. 2015 Jan;118:315-21. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.048. Chemosphere. 2015. PMID: 25463256
-
Microbial degradation of 4-monobrominated diphenyl ether in an aerobic sludge and the DGGE analysis of diversity.J Environ Sci Health B. 2010 Jul;45(5):379-85. doi: 10.1080/03601231003799945. J Environ Sci Health B. 2010. PMID: 20512728
-
Bacterial communities associated with aerobic degradation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from river sediments.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Mar;22(5):3810-9. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3626-9. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25269839
-
Review of contamination of sewage sludge and amended soils by polybrominated diphenyl ethers based on meta-analysis.Environ Pollut. 2017 Jan;220(Pt B):753-765. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.053. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Environ Pollut. 2017. PMID: 27814985 Review.
Cited by
-
Fast atrazine degradation by the mixed cultures enriched from activated sludge and analysis of their microbial community succession.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Oct;24(28):22152-22157. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9052-z. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28455570
References
-
- Talsness CE. Overview of toxicological aspects of polybrominated diphenyl ethers: a flame-retardant additive in several consumer products. Environmental Research. 2008;108(2):158–167. - PubMed
-
- Tokarz JA, III, Ahn M-Y, Leng J, Filley TR, Nies L. Reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in anaerobic sediment and a biomimetic system. Environmental Science and Technology. 2008;42(4):1157–1164. - PubMed
-
- He J, Robrock KR, Alvarez-Cohen L. Microbial reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) Environmental Science and Technology. 2006;40(14):4429–4434. - PubMed
-
- La Guardia MJ, Hale RC, Harvey E. Evidence of debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in biota from a wastewater receiving stream. Environmental Science and Technology. 2007;41(19):6663–6670. - PubMed
-
- Song M, Chu S, Letcher RJ, Seth R. Fate, partitioning, and mass loading of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) during the treatment processing of municipal sewage. Environmental Science and Technology. 2006;40(20):6241–6246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

