Child mortality estimation 2013: an overview of updates in estimation methods by the United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation
- PMID: 25013954
- PMCID: PMC4094389
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101112
Child mortality estimation 2013: an overview of updates in estimation methods by the United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation
Abstract
Background: In September 2013, the United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UN IGME) published an update of the estimates of the under-five mortality rate (U5MR) and under-five deaths for all countries. Compared to the UN IGME estimates published in 2012, updated data inputs and a new method for estimating the U5MR were used.
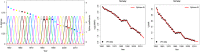
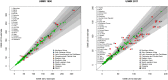
Methods: We summarize the new U5MR estimation method, which is a Bayesian B-spline Bias-reduction model, and highlight differences with the previously used method. Differences in UN IGME U5MR estimates as published in 2012 and those published in 2013 are presented and decomposed into differences due to the updated database and differences due to the new estimation method to explain and motivate changes in estimates.
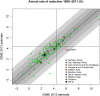
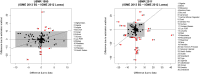
Findings: Compared to the previously used method, the new UN IGME estimation method is based on a different trend fitting method that can track (recent) changes in U5MR more closely. The new method provides U5MR estimates that account for data quality issues. Resulting differences in U5MR point estimates between the UN IGME 2012 and 2013 publications are small for the majority of countries but greater than 10 deaths per 1,000 live births for 33 countries in 2011 and 19 countries in 1990. These differences can be explained by the updated database used, the curve fitting method as well as accounting for data quality issues. Changes in the number of deaths were less than 10% on the global level and for the majority of MDG regions.
Conclusions: The 2013 UN IGME estimates provide the most recent assessment of levels and trends in U5MR based on all available data and an improved estimation method that allows for closer-to-real-time monitoring of changes in the U5MR and takes account of data quality issues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
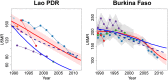
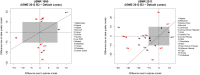
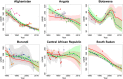
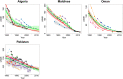
Similar articles
-
Child mortality estimation: a comparison of UN IGME and IHME estimates of levels and trends in under-five mortality rates and deaths.PLoS Med. 2012;9(8):e1001288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001288. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS Med. 2012. PMID: 22952434 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national trends in under-5 mortality between 1990 and 2019 with scenario-based projections until 2030: a systematic analysis by the UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation.Lancet Glob Health. 2022 Feb;10(2):e195-e206. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00515-5. Lancet Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 35063111 Free PMC article.
-
Progress toward global reduction in under-five mortality: a bootstrap analysis of uncertainty in Millennium Development Goal 4 estimates.PLoS Med. 2012;9(12):e1001355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001355. Epub 2012 Dec 11. PLoS Med. 2012. PMID: 23239945 Free PMC article.
-
Child mortality estimation: accelerated progress in reducing global child mortality, 1990-2010.PLoS Med. 2012;9(8):e1001303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001303. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS Med. 2012. PMID: 22952441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Child mortality estimation: methods used to adjust for bias due to AIDS in estimating trends in under-five mortality.PLoS Med. 2012;9(8):e1001298. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001298. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS Med. 2012. PMID: 22952437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Implications of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Viable Preterm Period.Am J Perinatol. 2020 Sep;37(11):1077-1083. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1713851. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Am J Perinatol. 2020. PMID: 32615621 Free PMC article.
-
Women's autonomy, neonatal, infant and under-five mortality in the Upper East Region of Ghana.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024 Sep 19;4(9):e0002776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0002776. eCollection 2024. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39298443 Free PMC article.
-
Are good intentions putting the vaccination ecosystem at risk?Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016 Sep;12(9):2469-74. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1172162. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 27269046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A formal representation of the WHO and UNICEF estimates of national immunization coverage: a computational logic approach.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047806. Epub 2012 Oct 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23133527 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of universal home visits on child health in Bauchi State, Nigeria: a stepped wedge cluster randomised controlled trial.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Oct 12;21(1):1085. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07000-3. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 34641865 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- United Nations (2013) The Millennium Development Goals Report 2013. New York: United Nations.
-
- Alkema L, New JR (2013) Global estimation of child mortality using a Bayesian B-spline bias-reduction method. arXiv: 1309.1602 [stat.AP]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1309.1602. Accessed 2013 Jun 20.
-
- Hill K, You D, Inoue M, Oestergaard MZ (2012) Technical Advisory Group of the United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (2012) Child Mortality Estimation: Accelerated Progress in Reducing Global Child Mortality, 1990–2010. PLoS Med 9(8): e1001303 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001303 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

