Sphingolipids and ceramides of mouse aqueous humor: Comparative profiles from normotensive and hypertensive DBA/2J mice
- PMID: 25014247
- PMCID: PMC4163522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.06.019
Sphingolipids and ceramides of mouse aqueous humor: Comparative profiles from normotensive and hypertensive DBA/2J mice
Abstract
Purpose: To identify the sphingolipid and ceramide species and their quantitative differences between normotensive and hypertensive intraocular pressure states in DBA/2J mouse aqueous humor (AH).
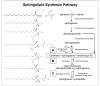
Methods: Normotensive and hypertensive AH was sampled from mice by paracentesis. Lipid extraction was performed using modifications of the Bligh and Dyer method. Protein concentration was estimated using the Bradford colorimetric assay. Sphingolipids and ceramides were identified and subjected to ratiometric quantification using appropriate class specific lipid standards on a TSQ Quantum Access Max triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
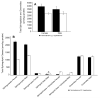
Results: The comparative profiles of normotensive and hypertensive DBA/2J mouse AH showed several species of sphingomyelin, sphingoid base, sphingoid base-1-phosphate (S1P) and ceramides common between them. A number of unique lipids in each of the above lipid classes were also identified in normotensive AH that were absent in hypertensive AH and vice versa.
Conclusion: A number of sphingolipid and ceramide species were found to be uniquely present in normotensive, but absent in hypertensive AH and vice versa. Further pursuit of these findings is likely to contribute towards expanding our understanding of the molecular changes associated with increased intraocular pressure (IOP) and glaucoma.
Keywords: Aqueous humor; Ceramides; Hypertensive; Mass spectrometry; Normotensive; Sphingolipids.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Morrison JC, Acott TS. Anatomy and physiology of aqueous humor outflow. In: Morrison JC, Pollack IP, editors. Glaucoma Science and Practice. Thieme Medical Publishers Inc.; New York: 2003. pp. 34–41.
-
- Mark HH. Aqueous humor dynamics in historical perspective. Surv Ophthalmol. 2010;55:89–100. - PubMed
-
- Civan MM, Macknight AD. The ins and outs of aqueous humour secretion. Exp Eye Res. 2004;78:625–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

