Outcome prediction in sepsis: speckle tracking echocardiography based assessment of myocardial function
- PMID: 25015102
- PMCID: PMC4227017
- DOI: 10.1186/cc13987
Outcome prediction in sepsis: speckle tracking echocardiography based assessment of myocardial function
Abstract
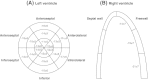
Introduction: Speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) is a relatively novel and sensitive method for assessing ventricular function and may unmask myocardial dysfunction not appreciated with conventional echocardiography. The association of ventricular dysfunction and prognosis in sepsis is unclear. We sought to evaluate frequency and prognostic value of biventricular function, assessed by STE in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock.
Methods: Over an eighteen-month period, sixty patients were prospectively imaged by transthoracic echocardiography within 24 hours of meeting severe sepsis criteria. Myocardial function assessment included conventional measures and STE. Association with mortality was assessed over 12 months.
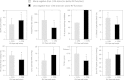
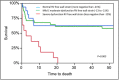
Results: Mortality was 33% at 30 days (n = 20) and 48% at 6 months (n = 29). 32% of patients had right ventricle (RV) dysfunction based on conventional assessment compared to 72% assessed with STE. 33% of patients had left ventricle (LV) dysfunction based on ejection fraction compared to 69% assessed with STE. RV free wall longitudinal strain was moderately associated with six-month mortality (OR 1.1, 95% confidence interval, CI, 1.02-1.26, p = 0.02, area under the curve, AUC, 0.68). No other conventional echocardiography or STE method was associated with survival. After adjustment (for example, for mechanical ventilation) severe RV free wall longitudinal strain impairment remained associated with six-month mortality.
Conclusion: STE may unmask systolic dysfunction not seen with conventional echocardiography. RV dysfunction unmasked by STE, especially when severe, was associated with high mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. LV dysfunction was not associated with survival outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Vincent J-L, Rhodes A, Perel A, Martin GS, Rocca Della G, Vallet B, Pinsky MR, Hofer CK, Teboul J-L, de Boode W-P, Scolletta S, Vieillard-Baron A, De Backer D, Walley KR, Maggiorini M, Singer M. Clinical review: Update on hemodynamic monitoring – a consensus of 16. Crit Care. 2011;15:229. doi: 10.1186/cc10291. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

