Integrating mapping-, assembly- and haplotype-based approaches for calling variants in clinical sequencing applications
- PMID: 25017105
- PMCID: PMC4753679
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3036
Integrating mapping-, assembly- and haplotype-based approaches for calling variants in clinical sequencing applications
Abstract
High-throughput DNA sequencing technology has transformed genetic research and is starting to make an impact on clinical practice. However, analyzing high-throughput sequencing data remains challenging, particularly in clinical settings where accuracy and turnaround times are critical. We present a new approach to this problem, implemented in a software package called Platypus. Platypus achieves high sensitivity and specificity for SNPs, indels and complex polymorphisms by using local de novo assembly to generate candidate variants, followed by local realignment and probabilistic haplotype estimation. It is an order of magnitude faster than existing tools and generates calls from raw aligned read data without preprocessing. We demonstrate the performance of Platypus in clinically relevant experimental designs by comparing with SAMtools and GATK on whole-genome and exome-capture data, by identifying de novo variation in 15 parent-offspring trios with high sensitivity and specificity, and by estimating human leukocyte antigen genotypes directly from variant calls.
Figures

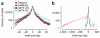

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

