The multifaceted nature of retinoid transport and metabolism
- PMID: 25019074
- PMCID: PMC4073323
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2014.05.04
The multifaceted nature of retinoid transport and metabolism
Abstract
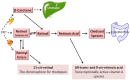
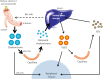
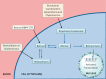
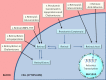
Since their discovery over a century ago, retinoids have been the most studied of the fat-soluble vitamins. Unlike most vitamins, retinoids are stored at relatively high concentrations in the body to buffer against nutritional insufficiency. Until recently, it was thought that the sole important retinoid delivery pathway to tissues involved retinol bound to retinol-binding protein (RBP4). More recent findings, however, indicate that retinoids can be delivered to tissues through multiple overlapping delivery pathways, involving chylomicrons, very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low density lipoprotein (LDL), retinoic acid bound to albumin, water soluble β-glucuronides of retinol and retinoic acid, and provitamin A carotenoids. This review will focus on explaining this evolving understanding of retinoid metabolism and transport within the body.
Keywords: Vitamin A; beta-carotene; hypervitaminosis A; hypovitaminosis A; metabolic disease; retinol-binding protein (RBP4); transthyretin (TTR).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overview of current knowledge of metabolism of vitamin A and carotenoids.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Dec;73(6):1375-9. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984. PMID: 6096622
-
Retinoid Homeostasis and Beyond: How Retinol Binding Protein 4 Contributes to Health and Disease.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 15;14(6):1236. doi: 10.3390/nu14061236. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35334893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological Functions of RBP4 and Its Relevance for Human Diseases.Front Physiol. 2021 Mar 11;12:659977. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.659977. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33790810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer and surface plasmon resonance-based assays for retinoid and transthyretin binding to retinol-binding protein 4.Anal Biochem. 2009 Sep 15;392(2):162-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2009.05.038. Epub 2009 May 29. Anal Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19482004
-
Functions of Intracellular Retinoid Binding-Proteins.Subcell Biochem. 2016;81:21-76. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-0945-1_2. Subcell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27830500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the STRA6 receptor for retinol uptake.Science. 2016 Aug 26;353(6302):aad8266. doi: 10.1126/science.aad8266. Science. 2016. PMID: 27563101 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A and Its Multi-Effects on Pancreas: Recent Advances and Prospects.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 18;12:620941. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.620941. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33679618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue- and sex-specific effects of β-carotene 15,15' oxygenase (BCO1) on retinoid and lipid metabolism in adult and developing mice.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Apr 15;572:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 17. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25602705 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting S100A9-ALDH1A1-Retinoic Acid Signaling to Suppress Brain Relapse in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2022 Apr 1;12(4):1002-1021. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0910. Cancer Discov. 2022. PMID: 35078784 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Retinoid X Receptors (RXRs) and dietary vitamin A in Alzheimer's disease: Evidence from clinicopathological and preclinical studies.Neurobiol Dis. 2021 Dec;161:105542. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105542. Epub 2021 Nov 1. Neurobiol Dis. 2021. PMID: 34737043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sporn MB, Dunlop NM, Newton DL, et al. Prevention of chemical carcinogenesis by vitamin A and its synthetic analogs (retinoids). Fed Proc 1976;35:1332-8 - PubMed
-
- Penniston KL, Tanumihardjo SA. The acute and chronic toxic effects of vitamin A. Am J Clin Nutr 2006;83:191-201 - PubMed
-
- Gudas JM, Sporn MB, Roberts AB. Cellular biology and biochemistry of the retinoids. In: Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS. eds. The Retinoids: Biology, Chemistry and Medicine. New York: Raven Press, 1994:443-520.
-
- Mangelsdorf DJ, Umesono K, Evans RM. The retinoid receptors. In: Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS. eds. The Retinoids: Biology, Chemistry and Medicine. New York: Rave Press, 1994:319-50.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
