Wireless monitoring of liver hemodynamics in vivo
- PMID: 25019160
- PMCID: PMC4097065
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102396
Wireless monitoring of liver hemodynamics in vivo
Abstract
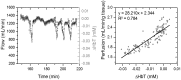
Liver transplants have their highest technical failure rate in the first two weeks following surgery. Currently, there are limited devices for continuous, real-time monitoring of the graft. In this work, a three wavelengths system is presented that combines near-infrared spectroscopy and photoplethysmography with a processing method that can uniquely measure and separate the venous and arterial oxygen contributions. This strategy allows for the quantification of tissue oxygen consumption used to study hepatic metabolic activity and to relate it to tissue stress. The sensor is battery operated and communicates wirelessly with a data acquisition computer which provides the possibility of implantation provided sufficient miniaturization. In two in vivo porcine studies, the sensor tracked perfusion changes in hepatic tissue during vascular occlusions with a root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.135 mL/min/g of tissue. We show the possibility of using the pulsatile wave to measure the arterial oxygen saturation similar to pulse oximetry. The signal is also used to extract the venous oxygen saturation from the direct current (DC) levels. Arterial and venous oxygen saturation changes were measured with an RMSE of 2.19% and 1.39% respectively when no vascular occlusions were induced. This error increased to 2.82% and 3.83% when vascular occlusions were induced during hypoxia. These errors are similar to the resolution of a commercial oximetry catheter used as a reference. This work is the first realization of a wireless optical sensor for continuous monitoring of hepatic hemodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures











References
-
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) and Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR). OPTN/SRTR 2011 Annual Data Report. Rockville, MD: Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration, Healthcare Systems Bureau, Division of Transplantation; 2012.
-
- Quiroga J, Colina I, Demetris AJ, Starzl TE, Van Thiel DH (1991) Cause and timing of first allograft failure in orthotopic liver transplantation: a study of 177 consecutive patients. Hepatology 14: 1054–1062. - PubMed
-
- Eghtesad B, Miller CM, Fung JJ (2009) Cleveland Clinic: Current clinical medicine, 2nd edition, “Post-liver transplantation management”. In: Carey WD, editor. Cleveland Clinic: Current clinical medicine, 2nd edition. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 564–570.
-
- Klar E, Bredt M, Kraus T, Angelescu M, Mehrabi A, et al. (1997) Early assessment of reperfusion injury by intraoperative quantification of hepatic microcirculation in patients. Transplant Proc 29: 362–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

