PKM2 regulates the Warburg effect and promotes HMGB1 release in sepsis
- PMID: 25019241
- PMCID: PMC4104986
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5436
PKM2 regulates the Warburg effect and promotes HMGB1 release in sepsis
Abstract
Increasing evidence suggests the important role of metabolic reprogramming in the regulation of the innate inflammatory response, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Here we provide evidence to support a novel role for the pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2)-mediated Warburg effect, namely aerobic glycolysis, in the regulation of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) release. PKM2 interacts with hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) and activates the HIF-1α-dependent transcription of enzymes necessary for aerobic glycolysis in macrophages. Knockdown of PKM2, HIF1α and glycolysis-related genes uniformly decreases lactate production and HMGB1 release. Similarly, a potential PKM2 inhibitor, shikonin, reduces serum lactate and HMGB1 levels, and protects mice from lethal endotoxemia and sepsis. Collectively, these findings shed light on a novel mechanism for metabolic control of inflammation by regulating HMGB1 release and highlight the importance of targeting aerobic glycolysis in the treatment of sepsis and other inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

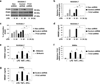
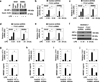

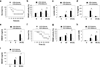
References
-
- Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:840–851. - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, et al. International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA. 2009;302:2323–2329. - PubMed
-
- Tracey KJ, et al. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987;330:662–664. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA, Thompson RC. Blocking IL-1: interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in vivo and in vitro. Immunol Today. 1991;12:404–410. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999;285:248–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

