Inflammation-based prognostic scores and nutritional prognostic index in patients with locally-advanced unresectable colorectal cancer
- PMID: 25022764
- PMCID: PMC4114089
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-210
Inflammation-based prognostic scores and nutritional prognostic index in patients with locally-advanced unresectable colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Unresectable colorectal cancer has a poor prognosis. However, some patients survive intensive chemotherapy, and complete resection of primary and metastatic tumors may even be possible. In the present study, we examined the prognostic factors associated with survival after intensive chemotherapy in patients with unresectable colorectal cancer.
Methods: This retrospective study enrolled 61 patients diagnosed with unresectable locally advanced colorectal cancer between January 2004 and December 2013. Among the prognostic parameters, we found that the prognoses of patients with abnormal performance status (PS) of 2 or 3, high Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS) of 1 or 2, high neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) >5, and low prognostic nutritional index (PNI) <40 were poor. Thus, we scored each patient according to our scoring system (abnormal PS, 2 or 3 = +1; high GPS, 1 or 2 = +1; high NLR, >5 = +1; and low PNI, <40 = +1). If the patient showed abnormalities in every parameter, the score would be +4.
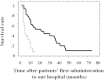
Results: Sixteen patients had a score of 0, 17 scored +1, 10 scored +2, 17 scored +3, and one scored +4. The median survival time (MST) of the 61 patients was 9 months. Patients were divided into two groups, a low-score group (0 and +1) and a high-score group (+2, +3, and +4). The MST of the 33 patients in the low-score group was significantly longer than that of the 28 patients in the high-score group (15 months versus 4 months, P < 0.001). Also, conversion chemotherapy was performed in 4.9% (3/61) of patients. And these 3 patients were in a low-score group.
Conclusions: This new prognostic scoring system may help to select patients with unresectable advanced colorectal cancer who are able to survive through intensive chemotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of selected inflammation-based prognostic markers in relapsed or refractory metastatic colorectal cancer patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 21;21(43):12410-20. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12410. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26604648 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic significance of the advanced lung cancer inflammation index in patients with unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2019 Mar 18;19(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5468-9. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30885163 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil count and the inflammation-based glasgow prognostic score predict survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer receiving first-line chemotherapy.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(2):945-50. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.2.945. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24568523
-
Are Markers of Systemic Inflammation Good Prognostic Indicators in Colorectal Cancer?Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2017 Dec;16(4):264-274. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28412137 Review.
-
Inflammation-Related Biomarkers for the Prediction of Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 27;22(15):8002. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158002. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preoperative geriatric nutritional risk index is a useful prognostic indicator in elderly patients with gastric cancer.Oncotarget. 2020 Jun 16;11(24):2345-2356. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27635. eCollection 2020 Jun 16. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32595832 Free PMC article.
-
Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Predicts Poor Prognosis of Patients After Curative Surgery for Gastric Cancer.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2021 May 3;1(2):43-52. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10007. eCollection 2021 May-Jun. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2021. PMID: 35403127 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic nutritional index as a predictor of survival in resectable gastric cancer patients with normal preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels: a propensity score matching analysis.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 13;18(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4201-4. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29534689 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of routine blood biomarkers in 3-year survival of resectable colorectal cancer patients: a prognostic nomogram for clinical practice.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2025 Mar 5;40(1):58. doi: 10.1007/s00384-025-04848-3. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2025. PMID: 40045061 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of prognostic markers for patients with curatively resected thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinomas.Mol Clin Oncol. 2016 Dec;5(6):767-772. doi: 10.3892/mco.2016.1073. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 28105355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer G, Papamichael D, Le Bail N, Louvet C, Hendler D, de Braud F, Wilson C, Morvan F, Bonetti A. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2938–2947. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Siena S, Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, Humblet Y, Bodoky G, Cunningham D, Jassem J, Rivera F, Kocákova I, Ruff P, Błasińska-Morawiec M, Šmakal M, Canon JL, Rother M, Oliner KS, Wolf M, Gansert J. Randomized, phase III trial of panitumumab with infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) versus FOLFOX4 alone as first-line treatment in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: the PRIME study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4697–4705. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.27.4860. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hwang JE, Kim HN, Kim DE, Choi HJ, Jung SH, Shim HJ, Bae WK, Hwang EC, Cho SH, Chung IJ. Prognostic significance of a systemic inflammatory response in patients receiving first-line palliative chemotherapy for recurred or metastatic gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:489. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-489. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Urba S, Gatz J, Shen W, Hossain A, Winfree K, Koustenis A, Peterson P, Cohen EE. Quality of life scores as prognostic factors of overall survival in advanced head and neck cancer: analysis of a phase III randomized trial of pemetrexed plus cisplatin versus cisplatin monotherapy. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:723–729. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.02.016. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical