Costs of staged versus simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a population-based study of the Taiwanese National Health Insurance Database
- PMID: 25023777
- PMCID: PMC4223718
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-014-0059-6
Costs of staged versus simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a population-based study of the Taiwanese National Health Insurance Database
Abstract
Background: Bilateral total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is required for many patients. There are few studies comparing the overall costs of staged and simultaneous bilateral TKA.
Methods: The Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) was searched, and the total medical costs of 452 patients who received simultaneous bilateral TKAs were compared with those of 690 who received staged bilateral TKAs.
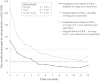
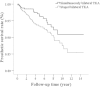
Results: All categories of medical costs were lower in the simultaneous TKA group, with the exception of therapeutic procedure fees which were higher in the simultaneous bilateral TKA group. The 10-year prosthesis survival rates for simultaneous and staged bilateral TKA were 90.9% and 87.5% (p > 0.05), respectively.
Conclusions: These results indicate that simultaneous bilateral TKA is more cost effective than staged bilateral TKA. Prosthesis survival is not affected by the choice for staged or simultaneous bilateral TKA.
Figures
Comment in
-
Morbidity and mortality after bilateral simultaneous total knee arthroplasty in a fast-track setting.Acta Orthop. 2016 Jun;87(3):286-90. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2016.1141631. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Acta Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26823094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McInnis DP, Devane PA, Horne G. Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: indications and complications. Curr Opin Orthop. 2003;14:52–57.
-
- Hu J, Liu Y, Lv Z, Li X, Qin X, Fan W. Mortality and morbidity associated with simultaneous bilateral or staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131:1291–1298. - PubMed
-
- Raviraj A, Chakravarthy M, Pai S, Prabhu A. Comparison of simultaneous bilateral and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty in terms of perioperative complications. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26:165–166. - PubMed
-
- Restrepo C, Parvizi J, Dietrich T, Einhorn TA. Safety of simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:1220–1226. - PubMed
-
- Ritter MA, Harty LD. Debate: simultaneous bilateral knee replacements: the outcomes justify its use. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;428:84–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

