Stromal response to Hedgehog signaling restrains pancreatic cancer progression
- PMID: 25024225
- PMCID: PMC4121834
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1411679111
Stromal response to Hedgehog signaling restrains pancreatic cancer progression
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is the most lethal of common human malignancies, with no truly effective therapies for advanced disease. Preclinical studies have suggested a therapeutic benefit of targeting the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway, which is activated throughout the course of PDA progression by expression of Hh ligands in the neoplastic epithelium and paracrine response in the stromal fibroblasts. Clinical trials to test this possibility, however, have yielded disappointing results. To further investigate the role of Hh signaling in the formation of PDA and its precursor lesion, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN), we examined the effects of genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of Hh pathway activity in three distinct genetically engineered mouse models and found that Hh pathway inhibition accelerates rather than delays progression of oncogenic Kras-driven disease. Notably, pharmacologic inhibition of Hh pathway activity affected the balance between epithelial and stromal elements, suppressing stromal desmoplasia but also causing accelerated growth of the PanIN epithelium. In striking contrast, pathway activation using a small molecule agonist caused stromal hyperplasia and reduced epithelial proliferation. These results indicate that stromal response to Hh signaling is protective against PDA and that pharmacologic activation of pathway response can slow tumorigenesis. Our results provide evidence for a restraining role of stroma in PDA progression, suggesting an explanation for the failure of Hh inhibitors in clinical trials and pointing to the possibility of a novel type of therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: Sonic hedgehog; cancer therapy; cerulein; hedgehog agonist; tumor stroma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
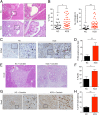
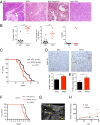

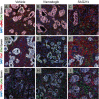
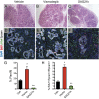
References
-
- Howlader N, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2010. Rockville, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2013.
-
- Anonymous StatBite. U.S. pancreatic cancer rates. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(24):1822. - PubMed
-
- Conroy T, et al. Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of Unicancer PRODIGE Intergroup FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(19):1817–1825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01CA117969-07/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA136574/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA1270003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA158640/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA133557-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136574/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155289/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R21CA158640-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01 CA117969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA155289-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM107615/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133557/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

