Intact thumb reflex in areflexic Guillain Barré syndrome: A novel phenomenon
- PMID: 25024572
- PMCID: PMC4090847
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-2327.132628
Intact thumb reflex in areflexic Guillain Barré syndrome: A novel phenomenon
Abstract
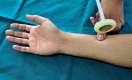
Introduction: Areflexia is one of the cardinal clinical features for the diagnosis of Guillain Barré syndrome. However, some patients may have sluggish proximal muscle stretch reflexes. Presence of thumb reflex, a distal stretch muscle reflex has not been documented in Guillain Barré syndrome.
Materials and methods: We prospectively evaluated thumb reflex in Guillain Barré syndrome patients and age matched controls from April to September 2013.
Results: There were 31 patients with Guillain Barré syndrome in whom thumb reflex could be elicited in all (24 brisk, 7 sluggish), whereas all the other muscle stretch reflexes were absent in 29 patients at presentation and the remaining two had sluggish biceps and quadriceps reflexes (P = 0.001). Serial examination revealed gradual diminution of the thumb reflex (P < 0.001). Rapid progression of weakness was associated with early loss of the thumb reflex.
Conclusion: Thumb reflex, a distal stretch reflex is preserved in the early phase of Guillain Barré syndrome.
Keywords: Acute flaccid paralysis; Guillain Barré syndrome; muscle stretch reflex; thumb reflex.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Asbury AK, Cornblath DR. Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for Guillain Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1990;27:S21–4. - PubMed
-
- Podnar S, Vodusek DB. Hyperreflexia in a patient with motor axonal Guillain-Barre syndrome. Eur J Neurol. 2000;7:727–30. - PubMed
-
- Campbell WW. 7th ed. New Delhi: Wolter Kluwer Pvt Ltd; 2013. Dejong's The Neurological Examination.
-
- Hughes RA, Newsom-Davis JM, Perkin GD, Pierce JM. Controlled trial prednisolone in acute polyneuropathy. Lancet. 1978;2:750–3. - PubMed
-
- Hadden RD, Cornblath DR, Hughes RA, Zielasek J, Hartung HP, Toyka KV, et al. Electrophysiological classification of Guillain Barre´ syndrome: Clinical associations and outcome. Plasma Exchange/Sandoglobulin Guillain-Barré Syndrome Trial Group. Ann Neurol. 1998;44:780–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

