Quality of diabetes care in primary health centres in north Al-batinah of oman
- PMID: 25024774
- PMCID: PMC4093660
- DOI: 10.2174/1874192401408010048
Quality of diabetes care in primary health centres in north Al-batinah of oman
Abstract
Objective: To assess the quality of diabetic care provided in primary health care settings in Oman.
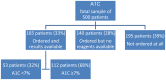
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study of randomly selected 500 patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) attending 6 primary care diabetic clinics in the north Al-Batinah region of Oman from January to December 2010. Nine standards on the quality of diabetes care were audited.
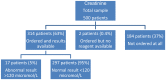
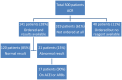
Results: The mean age of the sample was 51±13 years, ranging from 15 to 87 years; the majority (61%) were females. The mean duration of DM was 4±3 years, ranging from 1 to 18 years. Seventy-seven percent of the patients attended diabetic clinics at least 4 times per year. Of the 9 assessed diabetic standards, HbA1c was documented in 33% of the patients, body mass index in 12%, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in 40%, urinary albumin:creatinine ratio in 28%, creatinine in 63% and blood pressure (BP) in 96%. Optimal control among the documented indicators was noted in 32, 21, 25, 85, 95 and 19%, respectively. Twenty percent of the patients had their ECGs done while only 39% of the patients had foot examination. No patient had attained control in all of HbA1c., BP and LDL-C.
Conclusion: There is a gap between the recommended DM care guidelines and current practice with consequent poor quality of care in these patients.
Keywords: Arab; Oman; diabetes mellitus; diabetic standards; quality of care..
Figures
References
-
- Al-Lawati JA, Barakat N, Al-Zakwani I, Elsayed MK, Al-Maskari M, Al-Lawati M. Control of risk factors for cardiovascular disease among adults with previously diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus: a descriptive study from a middle eastern Arab population. Open Cardiovasc Med J. 2012;6:133–40. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran A, Chamukuttan S, Shetty SA, Arun N, Susairaj P. Obesity in Asia--is it different from rest of the world?. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012;28(Suppl 2 ):47–51. - PubMed
-
- Fowkes FG, Rudan D, Rudan I, Aboyans V, Denenberg JO, McDermott MM. Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: a systematic review and analysis. Lancet. 2013;382(9901):1329–40. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous