Delta neutrophil index as a prognostic marker of early mortality in gram negative bacteremia
- PMID: 25024871
- PMCID: PMC4091368
- DOI: 10.3947/ic.2014.46.2.94
Delta neutrophil index as a prognostic marker of early mortality in gram negative bacteremia
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is a syndrome that results in high morbidity and mortality. We investigated the delta neutrophil index (DN) as a predictive marker of early mortality in patients with gram-negative bacteremia.
Materials and methods: We conducted a retrospective study at a tertiary referral hospital in South Korea from November 2010 to March 2011. The DN was measured at onset of bacteremia and 24 hours and 72 hours later. The DN was calculated using an automatic hematology analyzer. Factors associated with 10-day mortality were assessed using logistic regression.
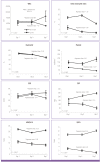
Results: A total of 172 patients with gram-negative bacteremia were included in the analysis; of these, 17 patients died within 10 days of bacteremia onset. In multivariate analysis, Sequental organ failure assessment scores (odds ratio [OR]: 2.24, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.31 to 3.84; P = 0.003), DN-day 1 ≥ 7.6% (OR: 305.18, 95% CI: 1.73 to 53983.52; P = 0.030) and DN-day 3 ≥ DN-day 1 (OR: 77.77, 95% CI: 1.90 to 3188.05; P = 0.022) were independent factors associated with early mortality in gram-negative bacteremia. Of four multivariate models developed and tested using various factors, the model using both DN-day 1 ≥ 7.6% and DN-day 3 ≥ DN-day 1 was most predictive early mortality.
Conclusions: DN may be a useful marker of early mortality in patients with gram-negative bacteremia. We found both DN-day 1 and DN trend to be significantly associated with early mortality.
Keywords: Bacteremia; Biological markers; Gram-negative bacterial infections; Mortality; Prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Delta neutrophil index: could it predict mortality in patients with bacteraemia?Scand J Infect Dis. 2012 Jul;44(7):475-80. doi: 10.3109/00365548.2012.657232. Epub 2012 Feb 19. Scand J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22339622
-
Red blood cell distribution width is an independent predictor of mortality in patients with gram-negative bacteremia.Shock. 2012 Aug;38(2):123-7. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31825e2a85. Shock. 2012. PMID: 22683729
-
Factors influencing mortality in abdominal solid organ transplant recipients with multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteremia.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Feb 27;17(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2276-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28241746 Free PMC article.
-
Early Intravenous Colistin Therapy as a Favorable Prognostic Factor for 28-day Mortality in Patients with CRAB Bacteremia: a Multicenter Propensity Score-Matching Analysis.J Korean Med Sci. 2019 Oct 14;34(39):e256. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e256. J Korean Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31602826 Free PMC article.
-
Short-course versus long-course antibiotic treatment in patients with uncomplicated gram-negative bacteremia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021 Feb;46(1):173-180. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13277. Epub 2020 Sep 27. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021. PMID: 32981149 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictors and outcomes of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy in critically ill patients.Acute Crit Care. 2020 May;35(2):67-76. doi: 10.4266/acc.2020.00024. Epub 2020 May 15. Acute Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32407613 Free PMC article.
-
Delta neutrophil index as a prognostic marker in emergent abdominal surgery.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Jul;33(6):e22895. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22895. Epub 2019 Apr 15. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 30985959 Free PMC article.
-
The delta neutrophil index is a prognostic factor for postoperative mortality in patients with sepsis caused by peritonitis.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 1;12(8):e0182325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182325. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28763506 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the delta neutrophil index with procalcitonin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein as predictors of sepsis in patients with acute prostatitis.Prostate Int. 2018 Dec;6(4):157-161. doi: 10.1016/j.prnil.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Prostate Int. 2018. PMID: 30505819 Free PMC article.
-
Delta neutrophil index (DNI) as a novel diagnostic and prognostic marker of infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Inflamm Res. 2017 Oct;66(10):863-870. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1066-y. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Inflamm Res. 2017. PMID: 28646289
References
-
- Levy MM, Dellinger RP, Townsend SR, Linde-Zwirble WT, Marshall JC, Bion J, Schorr C, Artigas A, Ramsay G, Beale R, Parker MM, Gerlach H, Reinhart K, Silva E, Harvey M, Regan S, Angus DC Surviving Sepsis Campaign. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign: results of an international guideline-based performance improvement program targeting severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:367–374. - PubMed
-
- Huttunen R, Aittoniemi J. New concepts in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of bacteremia and sepsis. J Infect. 2011;63:407–419. - PubMed
-
- Dickinson JD, Kollef MH. Early and adequate antibiotic therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2011;13:399–405. - PubMed
-
- Andaluz-Ojeda D, Bobillo F, Iglesias V, Almansa R, Rico L, Gandía F, Resino S, Tamayo E, de Lejarazu RO, Bermejo-Martin JF. A combined score of pro- and anti-inflammatory interleukins improves mortality prediction in severe sepsis. Cytokine. 2012;57:332–336. - PubMed
-
- Marshall JC, Reinhart K International Sepsis Forum. Biomarkers of sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:2290–2298. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

