Degradative actions of microbial xylanolytic activities on hemicelluloses from rhizome of Arundo donax
- PMID: 25024928
- PMCID: PMC4086442
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-014-0055-6
Degradative actions of microbial xylanolytic activities on hemicelluloses from rhizome of Arundo donax
Abstract
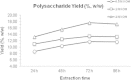
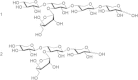
Polysaccharidases from extremophiles are remarkable for specific action, resistance to different reaction conditions and other biotechnologically interesting features. In this article the action of crude extracts of thermophilic microorganisms (Thermotoga neapolitana, Geobacillus thermantarcticus and Thermoanaerobacterium thermostercoris) is studied using as substrate hemicellulose from one of the most interesting biomass crops, the giant reed (Arundo donax L.). This biomass can be cultivated without competition and a huge amount of rhizomes remains in the soil at the end of cropping cycle (10-15 years) representing a further source of useful molecules. Optimization of the procedure for preparation of the hemicellulose fraction from rhizomes of Arundo donax, is studied. Polysaccharidases from crude extracts of thermophilic microorganisms revealed to be suitable for total degradative action and/or production of small useful oligosaccharides from hemicelluloses from A. donax. Xylobiose and interesting tetra- and pentasaccharide are obtained by enzymatic action in different conditions. Convenient amount of raw material was processed per mg of crude enzymes. Raw hemicelluloses and pretreated material show antioxidant activity unlike isolated tetra- and pentasaccharide. The body of results suggest that rhizomes represent a useful raw material for the production of valuable industrial products, thus allowing to increase the economic efficiency of A. donax cultivation.
Keywords: Arundo donax; Biorefinery; Thermophilic enzymes; Xylan; Xylanases; Xylooligosaccharides.
Figures
References
-
- Bernfeld P. In: Colowick S. Kaplan N, editor. Methods in Enzymology Academic Press, New York; 1955. Amylases α and β.
-
- Blois MS. Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature. 1958;4:1199–1200. doi: 10.1038/1811199a0. doi:10.1038/1811199a0. - DOI
-
- Bonanno G, Cirelli GL, Toscano A, Lo Giudice R, Pavone P. Heavy metal content in ash of energy crops growing in sewage-contaminated natural wetlands: potential applications in agriculture and forestry? Sci Total Environ. 2013;4:349–354. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.048. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.048. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;4:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Christakopoulosa P, Katapodisa P, Kalogerisa E, Kekosa D, Macrisa BJ, Stamatisb H, Skaltsac H. Antimicrobial activity of acidic xylo-oligosaccharides produced by family 10 and 11 endoxylanases. Int J Biol Macromol. 2003;4:171–175. doi: 10.1016/S0141-8130(02)00079-X. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0141-8130(02)00079-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

