Topiramate for weight reduction in adolescents with severe obesity
- PMID: 25027265
- PMCID: PMC5958908
- DOI: 10.1177/0009922814542481
Topiramate for weight reduction in adolescents with severe obesity
Abstract
Background: Medications for use as an adjunct to lifestyle modification therapy (LSM) for severe adolescent obesity are limited. Topiramate results in weight reduction in adults with obesity, but has not been studied in adolescents.
Objective: To examine the effect of topiramate plus LSM on body mass index (BMI) reduction in adolescents with severe obesity.
Methods: Data for this retrospective chart review were collected from patients attending a pediatric weight management program who were treated with LSM plus topiramate for 3 months minimum. Mean BMI percent change from baseline was evaluated using t-tests.
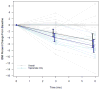
Results: Twenty-eight patients (mean age 15.2 ± 2.5 years, mean baseline BMI 46.2 ± 10.3 kg/m(2)) were identified for inclusion. The 6-month percent change in BMI was -4.9, 95% confidence interval (-7.1, -2.8), P < .001.
Conclusions: Topiramate with concurrent LSM was associated with clinically meaningful BMI reduction in adolescents with severe obesity. Randomized controlled clinical trials examining efficacy and safety of topiramate for severe obesity in adolescents are needed.
Keywords: adolescent; medication; obesity; pharmacotherapy; topiramate.
© The Author(s) 2014.
Figures
Comment in
-
Phentermine plus topiramate for weight reduction: more tolerable and effective?Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2015 Mar;54(3):302. doi: 10.1177/0009922814566935. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2015. PMID: 25589310 No abstract available.
-
Pharmacotherapy for Severe Obesity in Children.Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2015 Nov;54(13):1302. doi: 10.1177/0009922815580407. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2015. PMID: 25876922 No abstract available.
References
-
- Freedman DS, Mei Z, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS, Dietz WH. Cardiovascular risk factors and excess adiposity among overweight children and adolescents: The Bogalusa Heart Study. J Pediatr. 2007;150(1):12–17e2. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Wei R, Ogden CL, Freedman DS, Johnson CL, Curtin LR. Characterizing extreme values of body mass index-for-age by using the 2000 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention growth charts. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90(5):1314–1320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical