State-of-the-art of 3D cultures (organs-on-a-chip) in safety testing and pathophysiology
- PMID: 25027500
- PMCID: PMC4783151
- DOI: 10.14573/altex.1406111
State-of-the-art of 3D cultures (organs-on-a-chip) in safety testing and pathophysiology
Abstract
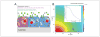
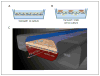
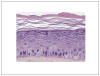
Integrated approaches using different in vitro methods in combination with bioinformatics can (i) increase the success rate and speed of drug development; (ii) improve the accuracy of toxicological risk assessment; and (iii) increase our understanding of disease. Three-dimensional (3D) cell culture models are important building blocks of this strategy which has emerged during the last years. The majority of these models are organotypic, i.e., they aim to reproduce major functions of an organ or organ system. This implies in many cases that more than one cell type forms the 3D structure, and often matrix elements play an important role. This review summarizes the state of the art concerning commonalities of the different models. For instance, the theory of mass transport/metabolite exchange in 3D systems and the special analytical requirements for test endpoints in organotypic cultures are discussed in detail. In the next part, 3D model systems for selected organs--liver, lung, skin, brain--are presented and characterized in dedicated chapters. Also, 3D approaches to the modeling of tumors are presented and discussed. All chapters give a historical background, illustrate the large variety of approaches, and highlight up- and downsides as well as specific requirements. Moreover, they refer to the application in disease modeling, drug discovery and safety assessment. Finally, consensus recommendations indicate a roadmap for the successful implementation of 3D models in routine screening. It is expected that the use of such models will accelerate progress by reducing error rates and wrong predictions from compound testing.
Figures




References
-
- Aardema MJ, Barnett BC, Khambatta Z, et al. International prevalidation studies of the EpiDerm 3D human reconstructed skin micronucleus (RSMN) assay: Transferability and reproducibility. Mutat Res. 2010;701:123–131. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2010.05.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aardema MJ, Barnett BB, Mun GC, et al. Evaluation of chemicals requiring metabolic activation in the EpiDerm 3D human reconstructed skin micronucleus (RSMN) assay. Mutat Res. 2013;750:40–49. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.08.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abbott A. Cell culture: Biology’s new dimension. Nature. 2003;424:870–872. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/424870a. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ackermann K, Borgia SL, Korting HC, et al. The Phenion full-thickness skin model for percutaneous absorption testing. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2010;23:105–112. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000265681. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahlenius H, Kokaia Z. Isolation and generation of neurosphere cultures from embryonic and adult mouse brain. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;633:241–252. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-019-5_18. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

