Effects of pitavastatin versus atorvastatin on the peripheral endothelial progenitor cells and vascular endothelial growth factor in high-risk patients: a pilot prospective, double-blind, randomized study
- PMID: 25027585
- PMCID: PMC4223413
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-014-0111-1
Effects of pitavastatin versus atorvastatin on the peripheral endothelial progenitor cells and vascular endothelial growth factor in high-risk patients: a pilot prospective, double-blind, randomized study
Abstract
Background: Circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) reflect endothelial repair capacity and may be a significant marker for the clinical outcomes of cardiovascular disease. While some high-dose statin treatments may improve endothelial function, it is not known whether different statins may have similar effects on EPCs.This study aimed to investigate the potential class effects of different statin treatment including pitavastatin and atorvastatin on circulating EPCs in clinical setting.
Methods: A pilot prospective, double-blind, randomized study was conducted to evaluate the ordinary dose of pitavastatin (2 mg daily) or atorvastatin (10 mg daily) treatment for 12 weeks on circulating EPCs in patients with cardiovascular risk such as hypercholesterolemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Additional in vitro study was conducted to clarify the direct effects of both statins on EPCs from the patients.
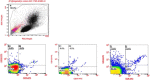
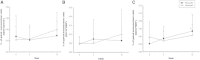
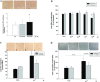
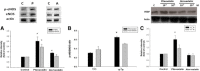
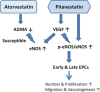
Results: A total of 26 patients (19 with T2DM) completed the study. While the lipid-lowering effects were similar in both treatments, the counts of circulating CD34+KDR+EPCs were significantly increased (from 0.021 ± 0.015 to 0.054 ± 0.044% of gated mononuclear cells, P < 0.05) only by pitavastatin treatment. Besides, plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine level was reduced (from 0.68 ± 0.10 to 0.53 ± 0.12 μmol/L, P < 0.05) by atorvastatin, and plasma vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) level was increased (from 74.33 ± 32.26 to 98.65 ± 46.64 pg/mL, P < 0.05) by pitavastatin. In the in vitro study, while both statins increased endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression, only pitavastatin increased the phosphorylation of eNOS in EPCs. Pitavastatin but not atorvastatin ameliorated the adhesion ability of early EPCs and the migration and tube formation capacities of late EPCs.
Conclusions: While both statins similarly reduced plasma lipids, only pitavastatin increased plasma VEGF level and circulating EPCs in high-risk patients, which is probably related to the differential pleiotropic effects of different statins.
Trial registration: This trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT01386853.
Figures
References
-
- Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Makuc DM, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, Moy CS, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Soliman EZ. et al.American heart association statistics committee and stroke statistics subcommittee: heart disease and stroke statistics–2012 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2012;125:e2–e220. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31823ac046. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Waters DD, Guyton JR, Herrington DM, McGowan MP, Wenger NK, Shear C. TNT steering committee members and investigators: treating to new targets (TNT) study: does lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels below currently recommended guidelines yield incremental clinical benefit? Am J Cardiol. 2004;93:154–158. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2003.09.031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fukushima Y, Daida H, Morimoto T, Kasai T, Miyauchi K, Yamagishi S, Takeuchi M, Hiro T, Kimura T, Nakagawa Y, Yamagishi M, Ozaki Y, Matsuzaki M. Relationship between advanced glycation end products and plaque progression in patients with acute coronary syndrome: the JAPAN-ACS sub-study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013;12:5. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

