Indian hedgehog signaling regulates transcription and expression of collagen type X via Runx2/Smads interactions
- PMID: 25028519
- PMCID: PMC4155658
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.570507
Indian hedgehog signaling regulates transcription and expression of collagen type X via Runx2/Smads interactions
Abstract
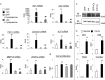
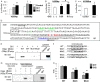
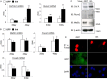
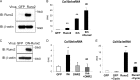
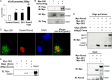
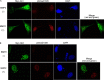
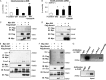
Indian hedgehog (Ihh) is essential for chondrocyte differentiation and endochondral ossification and acts with parathyroid hormone-related peptide in a negative feedback loop to regulate early chondrocyte differentiation and entry to hypertrophic differentiation. Independent of this function, we and others recently reported independent Ihh functions to promote chondrocyte hypertrophy and matrix mineralization in vivo and in vitro. However, the molecular mechanisms for these actions and their functional significance are still unknown. We recently discovered that Ihh overexpression in chondrocytes stimulated the expression of late chondrocyte differentiation markers and induced matrix mineralization. Focusing on collagen type X (Col10α1) expression and transcription, we observed that hedgehog downstream transcription factors GLI-Krüppel family members (Gli) 1/2 increased COL10A1 promoter activity and identified a novel Gli1/2 response element in the 250-bp basic promoter. In addition, we found that Ihh induced Runx2 expression in chondrocytes without up-regulating other modulators of chondrocyte maturation such as Mef2c, Foxa2, and Foxa3. Runx2 promoted Col10α1 expression in cooperation with Ihh. Further analyses using promoter assays, immunofluorescence, and binding assays showed the interaction of Gli1/2 in a complex with Runx2/Smads induces chondrocyte differentiation. Finally, we could demonstrate that Ihh promotes in vitro matrix mineralization using similar molecular mechanisms. Our data provide an in vitro mechanism for Ihh signaling to positively regulate Col10α1 transcription. Thus, Ihh signaling could be an important player for not only early chondrocyte differentiation but maturation and calcification of chondrocytes.
Keywords: Calcification; Chondrocyte; Col10a1; Differentiation; Gli1/Gli2-responsive Element; Hedgehog Signaling Pathway; Maturation; Runx2; Smads; Transcription.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β regulates expression of Indian hedgehog during chondrocytes differentiation.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 8;9(8):e104547. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104547. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25105964 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 governs differentiation stage-specific gene expression in growth plate chondrocytes via direct concomitant transactivation and repression.PLoS Genet. 2011 Nov;7(11):e1002356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002356. Epub 2011 Nov 3. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 22072985 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor Foxc1 is necessary for Ihh-Gli2-regulated endochondral ossification.Nat Commun. 2015 Mar 26;6:6653. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7653. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25808752
-
Runx2, an inducer of osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation.Histochem Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;149(4):313-323. doi: 10.1007/s00418-018-1640-6. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29356961 Review.
-
Smad-Runx interactions during chondrocyte maturation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S15-22. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11263661 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of an injury-induced skeletal progenitor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 11;112(32):9920-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1513066112. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26216955 Free PMC article.
-
Unique and overlapping GLI1 and GLI2 transcriptional targets in neoplastic chondrocytes.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 29;14(1):e0211333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211333. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30695055 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Hormone Signaling in the Development of the Endochondral Skeleton.Vitam Horm. 2018;106:351-381. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Vitam Horm. 2018. PMID: 29407442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regulatory Role of Signaling Crosstalk in Hypertrophy of MSCs and Human Articular Chondrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 14;16(8):19225-47. doi: 10.3390/ijms160819225. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26287176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gdf5 progenitors give rise to fibrocartilage cells that mineralize via hedgehog signaling to form the zonal enthesis.Dev Biol. 2015 Sep 1;405(1):96-107. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.06.020. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26141957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Crombrugghe B., Lefebvre V., Nakashima K. (2001) Regulatory mechanisms in the pathways of cartilage and bone formation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 721–727 - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg H. M. (2003) Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature 423, 332–336 - PubMed
-
- Gao B., Guo J., She C., Shu A., Yang M., Tan Z., Yang X., Guo S., Feng G., He L. (2001) Mutations in IHH, encoding Indian hedgehog, cause brachydactyly type A-1. Nat. Genet. 28, 386–388 - PubMed
-
- Lanske B., Karaplis A. C., Lee K., Luz A., Vortkamp A., Pirro A., Karperien M., Defize L. H., Ho C., Mulligan R. C., Abou-Samra A. B., Jüppner H., Segre G. V., Kronenberg H. M. (1996) PTH/PTHrP receptor in early development and Indian hedgehog-regulated bone growth. Science 273, 663–666 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

