Mycobacterium fortuitum and Polymicrobial Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 25028616
- PMCID: PMC4083769
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/323757
Mycobacterium fortuitum and Polymicrobial Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
Mycobacterium fortuitum is a ubiquitous, rapidly growing nontuberculous mycobacterium (NTM). It is the most commonly reported NTM in peritoneal dialysis (PD) associated peritonitis. We report a case of a 52-year-old man on PD, who developed refractory polymicrobial peritonitis necessitating PD catheter removal and shift to hemodialysis. Thereafter, M. fortuitum was identified in the PD catheter culture and in successive cultures of initial peritoneal effluent and patient was treated with amikacin and ciprofloxacin for six months with a good and sustained clinical response. Months after completion of the course of antibiotics, the patient successfully returned to PD. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of M. fortuitum peritonitis in the field of polymicrobial PD peritonitis. It demonstrates the diagnostic yield of pursuing further investigations in cases of refractory PD peritonitis. In a systematic review of the literature, only 20 reports of M. fortuitum PD peritonitis were identified. Similar to our case, a delay in microbiological diagnosis was frequently noted and the Tenckhoff catheter was commonly removed. However, the type and duration of antibiotic therapy varied widely making the optimal treatment unclear.
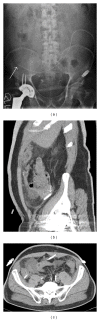
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium fortuitum as a cause of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis: case report and review of the literature.BMC Nephrol. 2012 Jun 8;13:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-35. BMC Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22682357 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic literature review of the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of peritoneal dialysis-related infection caused by nontuberculous mycobacteria.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Nov 28;25(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03841-2. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39609738 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium fortuitum Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis in a Child: A Case Report.Biomed Hub. 2024 Sep 13;9(1):128-133. doi: 10.1159/000541001. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Biomed Hub. 2024. PMID: 39474616 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium fortuitum peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis in a child: A case report and review of the literature.J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can. 2022 Jun 3;7(2):125-130. doi: 10.3138/jammi-2021-0029. eCollection 2022 Jun. J Assoc Med Microbiol Infect Dis Can. 2022. PMID: 36337360 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical course of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis due to non-tuberculosis mycobacterium - A single centre experience spanning 20 years.Perit Dial Int. 2022 Mar;42(2):204-211. doi: 10.1177/08968608211042434. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Perit Dial Int. 2022. PMID: 34477027
Cited by
-
Systemic Infection Caused by Mycobacterium fortuitum Following Aortic Valve Transplantation-Employing Combined Molecular Techniques for Accurate Species Identification.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Jun 14;82(8):335. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04313-y. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40515850
-
Mycobacterium wolinskyi Peritonitis after Peritoneal Catheter Embedment Surgery.Intern Med. 2017 Nov 15;56(22):3097-3101. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8871-17. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28943571 Free PMC article.
-
Septicemia and pneumonia due to Mycobacterium fortuitum infection in a patient with extronodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 May;96(18):e6800. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006800. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28471978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vas SI. Infections of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis catheters. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America. 1989;3(2):301–328. - PubMed
-
- White R, Abreo K, Flanagan R, et al. Nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 1993;22(4):581–587. - PubMed
-
- Li PK, Szeto CC, Piraino B, et al. Peritoneal dialysis-related infections recommendations: 2010 update. Peritoneal Dialysis International. 2010;30(4):393–423. - PubMed
-
- Soriano F, Rodriguez-Tudela JL, Gómez-Garcés JL, Velo M. Two possibly related cases of Mycobacterium fortuitum peritonitis associated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 1989;8(10):895–897. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

