An empirical study of different approaches for protein classification
- PMID: 25028675
- PMCID: PMC4084589
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/236717
An empirical study of different approaches for protein classification
Abstract
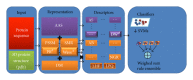
Many domains would benefit from reliable and efficient systems for automatic protein classification. An area of particular interest in recent studies on automatic protein classification is the exploration of new methods for extracting features from a protein that work well for specific problems. These methods, however, are not generalizable and have proven useful in only a few domains. Our goal is to evaluate several feature extraction approaches for representing proteins by testing them across multiple datasets. Different types of protein representations are evaluated: those starting from the position specific scoring matrix of the proteins (PSSM), those derived from the amino-acid sequence, two matrix representations, and features taken from the 3D tertiary structure of the protein. We also test new variants of proteins descriptors. We develop our system experimentally by comparing and combining different descriptors taken from the protein representations. Each descriptor is used to train a separate support vector machine (SVM), and the results are combined by sum rule. Some stand-alone descriptors work well on some datasets but not on others. Through fusion, the different descriptors provide a performance that works well across all tested datasets, in some cases performing better than the state-of-the-art.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An empirical study on the matrix-based protein representations and their combination with sequence-based approaches.Amino Acids. 2013 Mar;44(3):887-901. doi: 10.1007/s00726-012-1416-6. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Amino Acids. 2013. PMID: 23108592
-
High performance set of PseAAC and sequence based descriptors for protein classification.J Theor Biol. 2010 Sep 7;266(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.06.006. Epub 2010 Jun 15. J Theor Biol. 2010. PMID: 20558184
-
Set of approaches based on 3D structure and position specific-scoring matrix for predicting DNA-binding proteins.Bioinformatics. 2019 Jun 1;35(11):1844-1851. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty912. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30395157
-
Structural protein descriptors in 1-dimension and their sequence-based predictions.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2011 Sep;12(6):470-89. doi: 10.2174/138920311796957711. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2011. PMID: 21787299 Review.
-
Peptide bioinformatics: peptide classification using peptide machines.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;458:159-83. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-101-1_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 19065810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Consistency and variation of protein subcellular location annotations.Proteins. 2021 Feb;89(2):242-250. doi: 10.1002/prot.26010. Epub 2020 Sep 26. Proteins. 2021. PMID: 32935893 Free PMC article.
-
CpACpP: In Silico Cell-Penetrating Anticancer Peptide Prediction Using a Novel Bioinformatics Framework.ACS Omega. 2021 Jul 25;6(30):19846-19859. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02569. eCollection 2021 Aug 3. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34368571 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Protein-Protein Interactions via a Novel Matrix-Based Sequence Representation Model with Amino Acid Contact Information.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 24;17(10):1623. doi: 10.3390/ijms17101623. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27669239 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Protein-Protein Interactions from Amino Acid Sequences Based on Continuous and Discrete Wavelet Transform Features.Molecules. 2018 Apr 4;23(4):823. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040823. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29617272 Free PMC article.
-
Use Chou's 5-Step Rule to Predict DNA-Binding Proteins with Evolutionary Information.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 27;2020:6984045. doi: 10.1155/2020/6984045. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32775434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J, Li Y, Wang Q, et al. ProClusEnsem: predicting membrane protein types by fusing different models of pseudo amino acid composition. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2012;42(5):564–574. - PubMed
-
- Chou K-C, Shen H-B. MemType-2L: a Web server for predicting membrane proteins and their types by incorporating evolution information through Pse-PSSM. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2007;360(2):339–345. - PubMed
-
- Chou K-C, Shen H-B. Recent progress in protein subcellular location prediction. Analytical Biochemistry. 2007;370(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Chou K-C, Shen H-B. Signal-CF: a subsite-coupled and window-fusing approach for predicting signal peptides. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2007;357(3):633–640. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources