Transition state analysis of enantioselective Brønsted base catalysis by chiral cyclopropenimines
- PMID: 25029194
- PMCID: PMC4230825
- DOI: 10.1021/ja504532d
Transition state analysis of enantioselective Brønsted base catalysis by chiral cyclopropenimines
Abstract
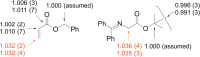
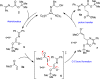
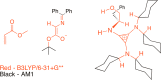
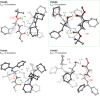
Experimental (13)C kinetic isotope effects have been used to interrogate the rate-limiting step of the Michael addition of glycinate imines to benzyl acrylate catalyzed by a chiral 2,3-bis(dicyclohexylamino) cyclopropenimine catalyst. The reaction is found to proceed via rate-limiting carbon-carbon bond formation. The origins of enantioselectivity and a key noncovalent CH···O interaction responsible for transition state organization are identified on the basis of density functional theory calculations and probed using experimental labeling studies. The resulting high-resolution experimental picture of the enantioselectivity-determining transition state is expected to guide new catalyst design and reaction development.
Figures


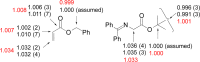

References
-
- Bandar J.; Lambert T. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5552–5555. - PubMed
-
- Bandar J. S.; Mazori A. Y.; Lambert T. H. Manuscript in preparation.
-
- Ishikawa T.; Araki Y.; Kumamoto T.; Seki H.; Fukuda K.; Isobe T. Chem. Commun. 2001, 245.
-
-
Several catalytic enantioselective Brønsted base catalyzed reactions are currently being developed using 1 and related catalysts. 1 is available as a salt from Sigma-Aldrich.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

