Association between serum selenium level and conversion of bacteriological tests during antituberculosis treatment
- PMID: 25029650
- PMCID: PMC4109199
- DOI: 10.1590/s1806-37132014000300010
Association between serum selenium level and conversion of bacteriological tests during antituberculosis treatment
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether serum selenium levels are associated with the conversion of bacteriological tests in patients diagnosed with active pulmonary tuberculosis after eight weeks of standard treatment.
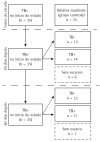
Methods: We evaluated 35 healthy male controls and 35 male patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, the latter being evaluated at baseline, as well as at 30 and 60 days of antituberculosis treatment. For all participants, we measured anthropometric indices, as well as determining serum levels of albumin, C-reactive protein (CRP) and selenium. Because there are no reference values for the Brazilian population, we used the median of the serum selenium level of the controls as the cut-off point. At 30 and 60 days of antituberculosis treatment, we repeated the biochemical tests, as well as collecting sputum for smear microscopy and culture from the patients.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 38.4 ± 11.4 years. Of the 35 patients, 25 (71%) described themselves as alcoholic; 20 (57.0%) were smokers; and 21 (60.0%) and 32 (91.4%) presented with muscle mass depletion as determined by measuring the triceps skinfold thickness and arm muscle area, respectively. Of 24 patients, 12 (39.2%) were classified as moderately or severely emaciated, and 15 (62.5%) had lost > 10% of their body weight by six months before diagnosis. At baseline, the tuberculosis group had lower serum selenium levels than did the control group. The conversion of bacteriological tests was associated with the CRP/albumin ratio and serum selenium levels 60 days after treatment initiation.
Conclusions: Higher serum selenium levels after 60 days of treatment were associated with the conversion of bacteriological tests in pulmonary tuberculosis patients.
Objetivo:: Determinar se os níveis séricos de selênio estão associados à conversão dos testes bacteriológicos em pacientes diagnosticados com tuberculose pulmonar ativa após oito semanas de tratamento-padrão.
Métodos:: No início do estudo, avaliamos 35 controles saudáveis, do sexo masculino, e 35 pacientes do sexo masculino com tuberculose pulmonar. Estes foram também avaliados após 30 e 60 dias de tratamento antituberculose. Todos os participantes submeteram-se a medições antropométricas e quantificação dos níveis séricos de albumina, proteína C reativa (PCR) e selênio. Como não há valores de referência para a população brasileira, usamos a mediana dos resultados de selênio sérico dos controles como ponto de corte. Aos 30 e 60 dias do tratamento antituberculose, todos os testes bioquímicos foram repetidos, e foram coletadas amostras de escarro para baciloscopia e cultura.
Resultados:: A média de idade dos pacientes foi de 38,4 ± 11.4 anos. Dos 35 pacientes, 25 (71,0%) referiram alcoolismo, 20 (57,0%) eram fumantes, e 21 (60,0%) e 32 (91,4%) apresentavam depleção muscular pela medição da dobra cutânea tricipital e da área muscular do braço, respectivamente. De 24 pacientes, 12 (39,2%) foram classificados em moderadamente ou gravemente magros, e 15 (62,5%) apresentaram perda de peso > 10% em até seis meses antes do diagnóstico. No início do estudo, o grupo com tuberculose apresentou menores níveis de selênio sérico que os controles. A conversão dos testes bacteriológicos associou-se à relação PCR/albumina e aos níveis de selênio sérico 60 dias após o início do tratamento.
Conclusões:: Níveis maiores de selênio sérico após 60 dias de tratamento associaram-se à conversão bacteriológica em pacientes com tuberculose pulmonar.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2011. Geneva: World Health Organization; [2013 May 8]. 2011. 258. a Available from: http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/2011/gtbr11_full.pdf.
-
- Wallis RS, Kim P, Cole S, Hanna D, Andrade BB, Maeurer M, et al. Tuberculosis biomarkers discovery: developments, needs, and challenges. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(4):362–372. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70034-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lönnroth K, Jaramillo E, Williams BG, Dye C, Raviglione M. Drivers of tuberculosis epidemics: the role of risk factors and social determinants. Soc Sci Med. 2009;68(12):2240–2246. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.03.041 - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Lettow M, Harries AD, Kumwenda JJ, Zijlstra EE, Clark TD, Taha TE, et al. Micronutrient malnutrition and wasting in adults with pulmonary tuberculosis with and without HIV co-infection in Malawi. BMC Infect Dis. 2004;4(1):61–61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-4-61 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seyedrezazadeh E, Ostadrahimi A, Mahboob S, Assadi Y, Ghaemmagami J, Pourmogaddam M. Effect of vitamin E and selenium supplementation on oxidative stress status in pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Respirology. 2008;13(2):294–298. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1843.2007.01200.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

