Organismal proteostasis: role of cell-nonautonomous regulation and transcellular chaperone signaling
- PMID: 25030693
- PMCID: PMC4102760
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.241125.114
Organismal proteostasis: role of cell-nonautonomous regulation and transcellular chaperone signaling
Abstract
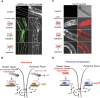
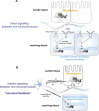
Protein quality control is essential in all organisms and regulated by the proteostasis network (PN) and cell stress response pathways that maintain a functional proteome to promote cellular health. In this review, we describe how metazoans employ multiple modes of cell-nonautonomous signaling across tissues to integrate and transmit the heat-shock response (HSR) for balanced expression of molecular chaperones. The HSR and other cell stress responses such as the unfolded protein response (UPR) can function autonomously in single-cell eukaryotes and tissue culture cells; however, within the context of a multicellular animal, the PN is regulated by cell-nonautonomous signaling through specific sensory neurons and by the process of transcellular chaperone signaling. These newly identified forms of stress signaling control the PN between neurons and nonneuronal somatic tissues to achieve balanced tissue expression of chaperones in response to environmental stress and to ensure that metastable aggregation-prone proteins expressed within any single tissue do not generate local proteotoxic risk. Transcellular chaperone signaling leads to the compensatory expression of chaperones in other somatic tissues of the animal, perhaps preventing the spread of proteotoxic damage. Thus, communication between subcellular compartments and across different cells and tissues maintains proteostasis when challenged by acute stress and upon chronic expression of metastable proteins. We propose that transcellular chaperone signaling provides a critical control step for the PN to maintain cellular and organismal health span.
Keywords: C. elegans; chaperones; proteostasis; stress response; transcellular stress signaling.
© 2014 van Oosten-Hawle and Morimoto; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Acosta-Alvear D, Zhou Y, Blais A, Tsikitis M, Lents NH, Arias C, Lennon CJ, Kluger Y, Dynlacht BD 2007. XBP1 controls diverse cell type- and condition-specific transcriptional regulatory networks. Mol Cell 27: 53–66 - PubMed
-
- Antebi A, Culotti JG, Hedgecock EM 1998. daf-12 regulates developmental age and the dauer alternative in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 125: 1191–1205 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
