Chromosome imbalance as a driver of sex disparity in disease
- PMID: 25031659
- PMCID: PMC4091450
- DOI: 10.7150/jgen.8123
Chromosome imbalance as a driver of sex disparity in disease
Abstract
It has long been recognized that men and women exhibit different risks for diverse disorders ranging from metabolic to autoimmune diseases. However, the underlying causes of these disparities remain obscure. Analysis of patients with chromosomal abnormalities, including Turner syndrome (45X) and Klinefelter syndrome (47XXY), has highlighted the importance of X-linked gene dosage as a contributing factor for disease susceptibility. Escape from X-inactivation and X-linked imprinting can result in transcriptional differences between normal men and women as well as in patients with sex chromosome abnormalities. Animal models support a role for X-linked gene dosage in disease with O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT) emerging as a prime candidate for a pleiotropic effector. OGT encodes a highly regulated nutrient-sensing epigenetic modifier with established links to immunity, metabolism and development.
Keywords: Klinefelter syndrome; O-GlcNAcylation; Turner syndrome; dosage compensation; imprinting.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
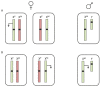



References
-
- Stochholm K, Juul S, Juel K, Naeraa RW, Gravholt CH. Prevalence, incidence, diagnostic delay, and mortality in Turner syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3897–902. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-0558. - PubMed
-
- Ranke MB, Saenger P. Turner's syndrome. The Lancet. 2001;358:309–14. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(01)05487-3. - PubMed
-
- Bondy CA, Cheng C. Monosomy for the X chromosome. Chromosome Research. 2009;17:649–58. doi:10.1007/s10577-009-9052-z. - PubMed
-
- Lynn PMY, Davies W. The 39,XO mouse as a model for the neurobiology of Turner syndrome and sex-biased neuropsychiatric disorders. Behavioural Brain Research. 2007;179:173–82. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2007.02.013. - PubMed
-
- Carrel L, Willard HF. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature. 2005;434:400–4. doi:10.1038/nature03479. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

